Summary: Discover how OCR technology can streamline your accounts payable process. Automate data entry, reduce errors, and improve efficiency with OCR invoice processing.
Ever found yourself drowning in a pile of invoices, desperately trying to process them while fighting off errors that slip through despite your team’s best efforts? I know this struggle well—it's one that countless accounting teams face daily. In fact, a recent Gartner survey showed that 59% of accountants make several financial errors each month, with nearly a third admitting to mistakes every week.
But here’s the good news: there's a smarter way to tackle this challenge. Imagine automating this time-consuming and error-prone process. No more manual data entry, lost invoices, or expensive mistakes. That’s where OCR (Optical Character Recognition) for accounts payable comes in. This powerful technology scans documents like invoices, extracts the relevant data, and converts it into a digital, editable format.
By embracing the paperless accounts payable process, you can eliminate manual intervention, reduce errors, and gain greater control over your AP workflow.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through how OCR invoice processing works and why it could be a game-changer for your business. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the technology, its benefits, and how you can start integrating it into your accounts payable process.

What is OCR for accounts payable?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a technology that enables computers to recognize and extract text from scanned documents, images, and PDFs. OCR has been around since the early days of computing, with the first commercial OCR system introduced in the 1950s. Since then, OCR technology has evolved significantly, with modern solutions leveraging advanced techniques like machine learning and artificial intelligence to improve accuracy and efficiency.
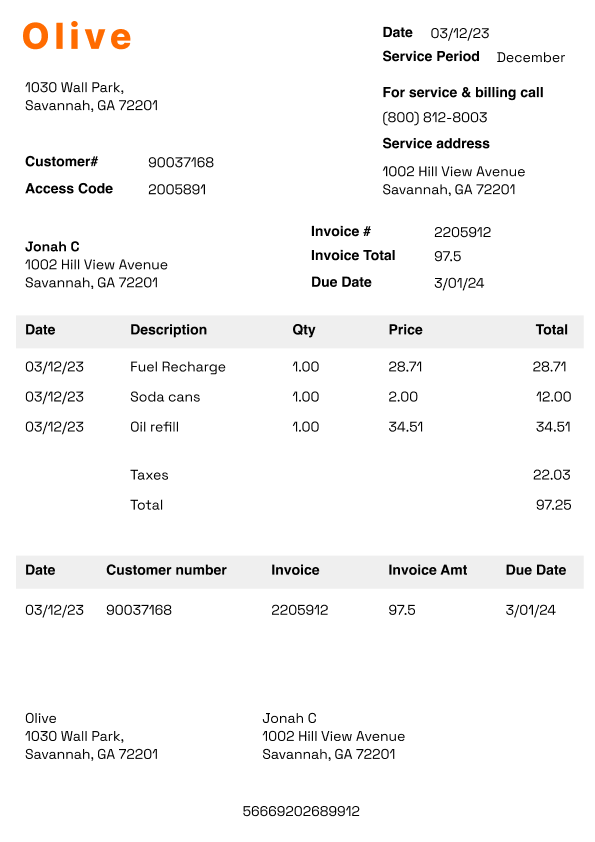
In the accounts payable (AP) context, OCR helps capture and digitize data from invoices, Purchase Orders, Purchase Requisitions, and Goods Received Notes. It can read and extract fields such as vendor names, invoice numbers, amounts, and due dates from a wide range of documents, including printed documents (e.g., contracts, forms, invoices), scanned images, photographs of text, and image-only PDFs.
The role of OCR in the accounts payable process
The accounts payable process involves receiving invoices from suppliers, verifying the accuracy of the invoices, approving payments, and ultimately paying the suppliers for the goods or services provided.
Now, here's the thing: many companies still use manual data entry for their accounts payable process. They open up each invoice, manually key in the data into their accounting system, and then file the invoice away. It's not just time-consuming, it's also highly inefficient.
Think about it:
- How many hours have you wasted on manual data entry, trying to decipher illegible handwriting, or chasing down missing invoice details?
- How often have you lost or misplaced an invoice, leading to late payments, missed discounts, or strained vendor relationships?
- How much visibility do you really have in your AP performance when all your data is trapped in paper documents and spreadsheets?
If any of this sounds familiar, it's time to consider OCR for accounts payable. Traditional OCR solutions can help streamline invoice processing to a certain extent. These tools use pattern recognition to match characters in an invoice image to predefined templates, enabling data extraction from structured invoices.
However, traditional OCR may fall short when it comes to more complex, unstructured invoices. Invoices come in various formats, layouts, and quality levels, often containing handwritten notes, stamps, or logos that can confuse traditional OCR engines. As a result, these tools may require significant manual intervention to validate and correct the extracted data, slowing down your AP process and potentially introducing errors.
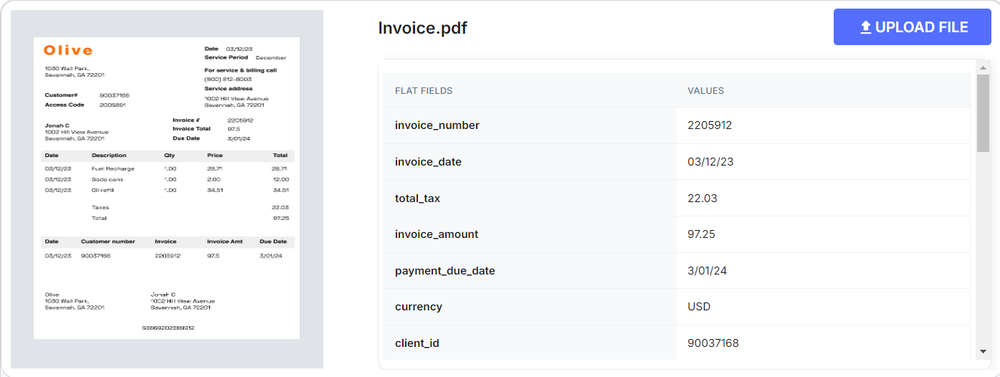
That's where advanced OCR solutions come in. Built-in AI and ML models help these tools learn and adapt to different invoice formats over time, improving their accuracy and reducing the need for manual corrections. AI-powered OCR can automatically extract data from invoices, reducing manual data entry and minimizing the risk of errors or lost invoices.
How does OCR accounts payable work
From faster processing times to greater visibility into your AP performance, OCR can help you on multiple fronts. If macroeconomic pressures are forcing you to do more with less, advanced OCR can help you produce quick wins that improve your bottom line without adding headcount.
So, how exactly does OCR work in accounts payable? Firstly, you'd need an accounts payable OCR software or AP invoice OCR solution. These tools read and extract data from your invoices, regardless of format or layout.
Let's take a closer look at the OCR process, step by step, along with actionable tips to optimize each stage of the process:
1. Invoice capture
The OCR process begins with capturing the data from invoices, purchase orders, and goods received notes. This can be done by scanning physical documents using a high-quality scanner or uploading files (such as PDFs or images) directly to your OCR software.
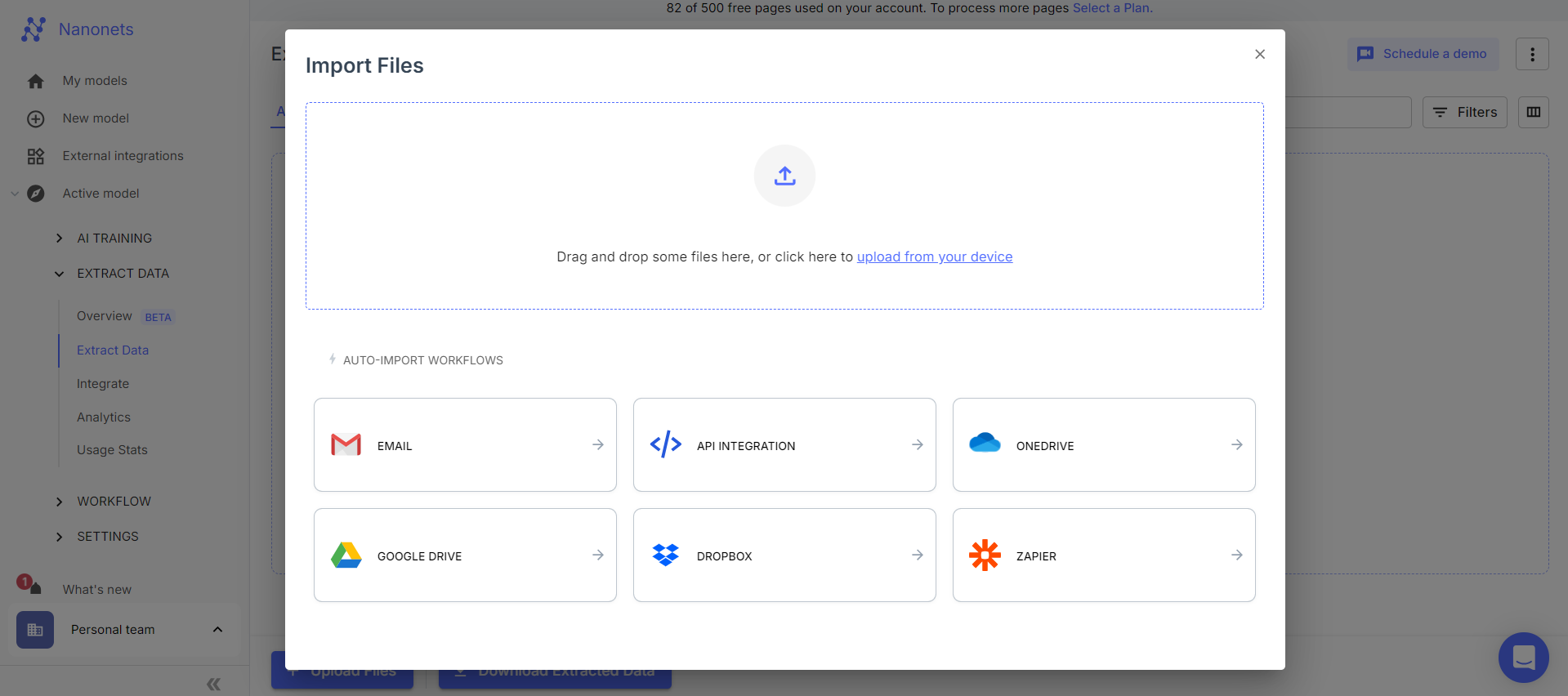
To ensure the best possible results, use a scanner with a resolution of 300 dpi or higher to capture small text and fine details accurately. If you use a mobile to scan the document, ensure it is clean. The image should be captured in a well-lit space and free from distortions, shadows, or background noise that could interfere with OCR accuracy.
2. Image preprocessing
Once the documents are captured, the OCR software prepares the images for text recognition. This may involve image enhancement, noise removal, and orientation correction to ensure the highest possible accuracy.

Some OCR software can automatically detect and correct skewed pages or remove borders that may interfere with text recognition, particularly useful for invoices and other AP documents that may not always be perfectly aligned.
Avoid using bitonal output if the original document has low contrast or poor quality, as this can significantly reduce OCR accuracy. Stick to grayscale or color images when possible.
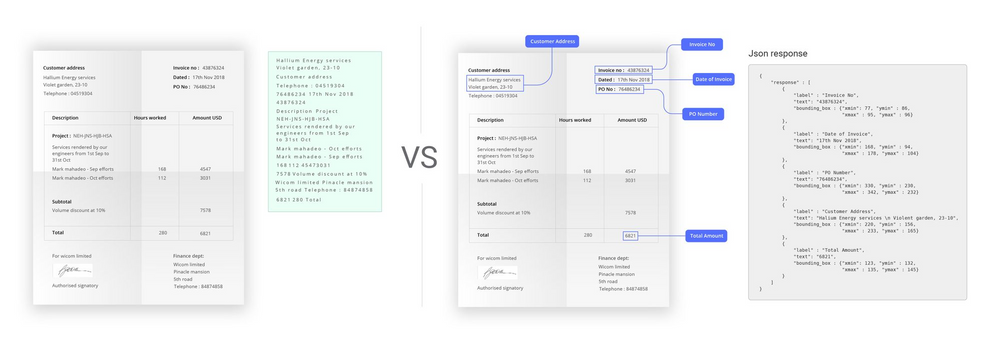
3. Document classification and data extraction
Once the invoices are in the system, the OCR engine gets to work. It automatically identifies and classifies different types of documents. For example, an organization dealing with invoices, receipts, and purchase orders can automatically categorize incoming documents based on their content. The OCR engine is trained on sample documents and learns to recognize distinguishing features of each document type.
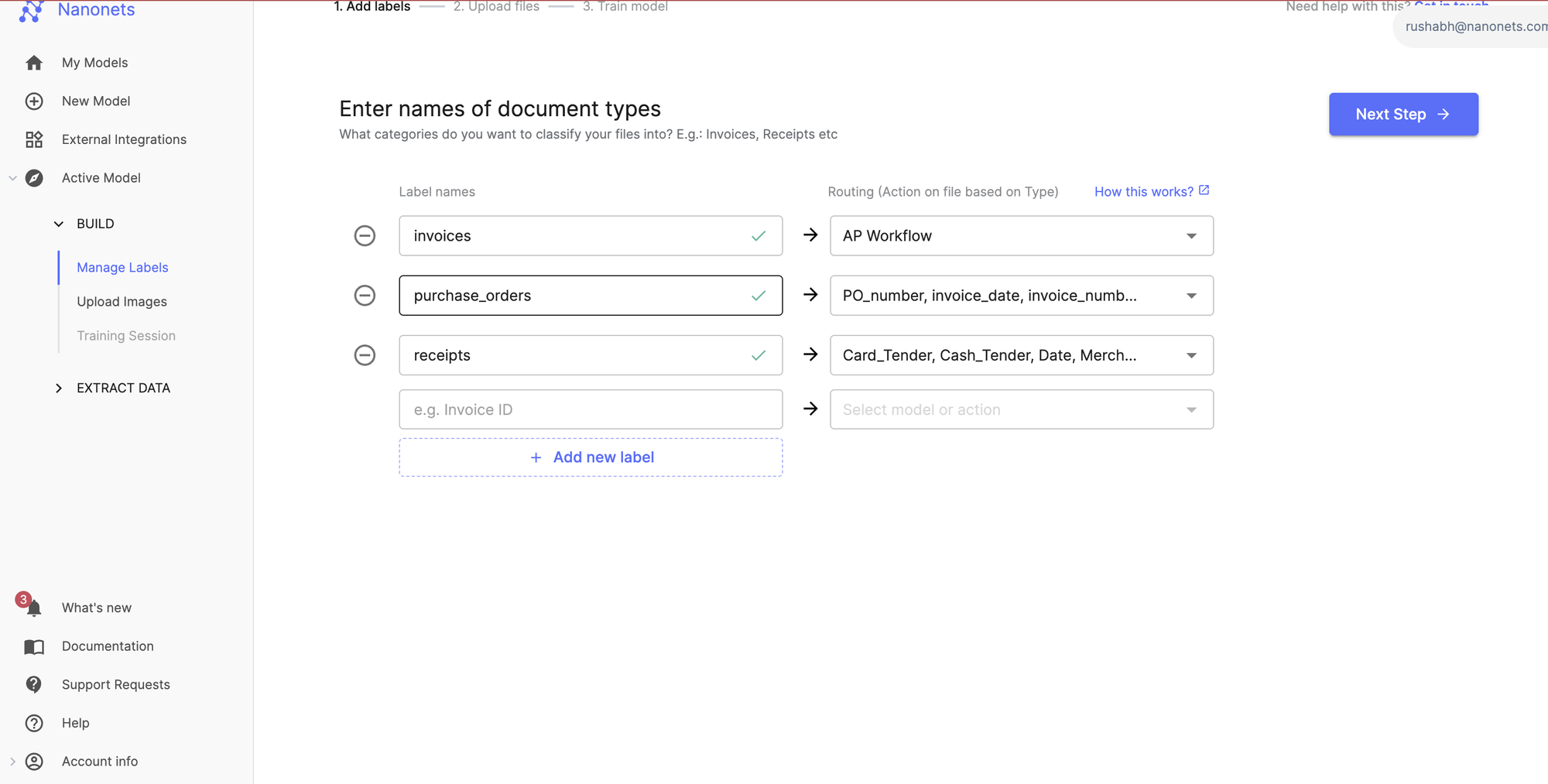
Once classified, the documents can be sent to the right OCR engine for data extraction. This is especially handy when you are processing AP documents in bulk.
The OCR engine then will extract fields like:
- Invoice number and date
- Vendor name and address
- Line item details (quantity, description, unit price)
- Total amount due
- Tax amounts and rates
- Payment terms and due date
To enhance the accuracy of the recognition process, you can standardize invoice and purchase order formats in collaboration with vendors, using consistent layouts, fonts, and data placement. Also, consider employing specialized training data or dictionaries that include industry-specific terminology and ensure that the OCR software supports your documents' language(s) with appropriate lexical data.
4. Data validation and exception handling
Of course, even the most advanced OCR needs human-in-the-loop data validation to ensure accuracy, avoid duplicates, and handle edge cases (such as heavily damaged documents or handwritten notes on invoices).
So, after the data is extracted, it undergoes a validation process. The OCR software checks the extracted information against predefined rules and flags any discrepancies or missing data.
For example:
- Flagging invoices over a certain dollar threshold
- Flagging invoices from new or unknown vendors
- Flagging invoices that are duplicates of previously processed ones
- Flagging invoices where the line items don't match the corresponding purchase order
These validation rules help catch errors and exceptions early in the process, preventing incorrect payments and reducing the need for costly corrections down the line. The flagged invoices are routed to the appropriate AP team member for review and correction, while the rest can proceed straight through to payment processing.
To enhance the process, you can implement cross-referencing of the extracted information with other sources, such as matching invoice data with corresponding purchase orders or goods received notes, to identify and correct any errors. Remove unwanted characters, white spaces, and spelling correction to streamline the validation of vendor names, addresses, and other key details.
5. Data export
Once validated, you need to export and integrate the data with your existing accounts payable systems and ERPs. OCR software lets you automate the process, enabling seamless data flow between your systems and eliminating the need for manual data entry. It ensures that your financial systems are always up-to-date.
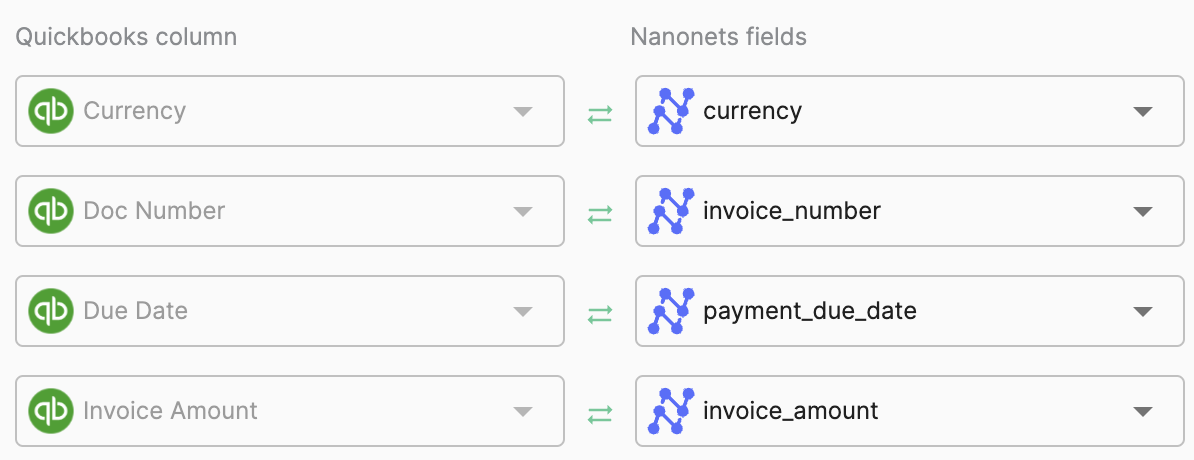
You should train your accounts payable staff to use and integrate your OCR solution with your existing systems, emphasizing the importance of maintaining consistent data formats and handling exceptions.
6. Archiving
Finally, the processed documents are archived for future reference and auditing purposes. When archiving, consider the best file format for your project based on your research needs and accessibility requirements. Searchable PDFs may be suitable to view the original layout of invoices, purchase orders, or goods received notes while also enabling search and copy-paste functionality.
Develop a consistent file naming convention that includes key details like vendor name, document type, and date, and organize your archived files in a logical folder structure for easy retrieval.
Remember to regularly monitor and analyze the performance of your OCR solution, tracking key metrics and identifying areas for improvement to continuously refine your process over time.
What are the key benefits of implementing OCR in your AP processes?
From reducing manual data entry to integration OCR can transform your accounts payable function. The technology enables your AP department to shift from a reactive, transaction-focused cost center to a proactive, strategic business center that drives value and supports organizational growth.
Let's take a closer look at some of the key advantages:
1. Automated data extraction and reduced manual effort
Implementing OCR technology can dramatically improve your AP team's productivity. For example, one company's AP team spent 1,040 hours (approximately four months) per year on manual data entry, hindering their efficiency. After adopting an advanced OCR solution, they were able to process all their weekly invoices in a single day, reducing manual data entry by up to 90% and saving valuable time and resources.
Automatically extracting critical information from invoices, purchase orders, and goods received notes enables your team to handle a higher volume of transactions more efficiently.
2. Increased processing speed
Automating data extraction and validation with OCR empowers your accounts payable team to process invoices significantly faster than manual methods. A recent study found that companies with fully automated AP processes handle more than double the workload, processing 18,649 invoices per full-time employee annually, compared to just 8,689 for those relying on manual methods.
This increased efficiency enables your team to meet payment deadlines, avoid late fees, and capitalize on early payment discounts, ultimately improving your bottom line.
3. Improved accuracy and reduced errors
Minimizing manual intervention with OCR helps reduce the risk of human errors, such as typos, duplications, or misinterpretation of data. Gartner research shows that companies with high technology acceptance can reduce these financial mistakes by 75%.
This helps prevent discrepancies or inconsistencies early in the process, allowing for prompt resolution and preventing errors from propagating downstream. Moreover, it enables to the finance team to make realistic cash flow projections and forecasts based on accurate data.
4. Enhanced visibility into AP processes
In a manual account payable processing setup, invoice data may often be scattered across paper documents, email attachments, local devices, and cloud storage. Gathering and analyzing invoice information from all these places becomes time-consuming and error-prone.
Meanwhile, with OCR, companies can automatically extract and digitize invoice data from various sources, centralizing it into a searchable and analyzable format like a spreadsheet. This centralization empowers AP teams to quickly access and review invoice information, monitor key metrics, and identify trends or discrepancies. Moreover, it makes filing, storing, and maintaining them easier for audit or regulatory purposes.
5. Achieve significant cost savings
Advanced OCR solutions can reduce average invoice processing costs from $40.70 to just $3.34 and decrease turnaround time from 16.3 days to a mere 3.8 days. This increased efficiency not only helps reduce labor costs but also helps you avoid late payment penalties and capture early payment discounts.
Moreover, by digitizing your invoices, OCR minimizes the need for paper, physical storage space, and transportation costs associated with manual AP processing, further contributing to cost savings and promoting environmental sustainability.
6. Enhanced data validation and compliance
OCR solutions often include built-in validation rules and checks to ensure the accuracy and completeness of extracted data. By automatically flagging discrepancies, missing information, or potential duplicates, OCR helps maintain the integrity of your financial data and ensures compliance with internal policies and external regulations.
7. Faster month-end closing and financial reporting
By automating data extraction and validation, OCR provides your accounting team with faster access to accurate financial data. This enables them to generate reports, reconcile accounts, and close the books more efficiently, saving valuable time and effort.
A recent study found that nearly 60% of organizations with automated data extraction and reconciliations managed to close their quarterly books within six working days, compared to just 38% without automation. This faster closing process lets your team focus on strategic initiatives and make informed business decisions based on timely financial insights.
Limitations of AP invoice OCR and how to overcome them with advanced OCR
While OCR technology offers significant benefits for accounts payable processes, it's essential to be aware of its limitations and the challenges that may arise during implementation. By understanding these limitations and leveraging advanced OCR tools, you can ensure a smooth transition and maximize the value of your OCR investment.
1. Inaccurate data extraction from poor-quality documents
In an AP context, your OCR software may need to accurately extract data from invoices that are poorly printed formatted, have faded text, or contain handwritten information. A traditional OCR may struggle to accurately capture data from such documents, leading to incorrect or incomplete data capture. You will have to manually intervene to correct errors – slowing down the AP process.
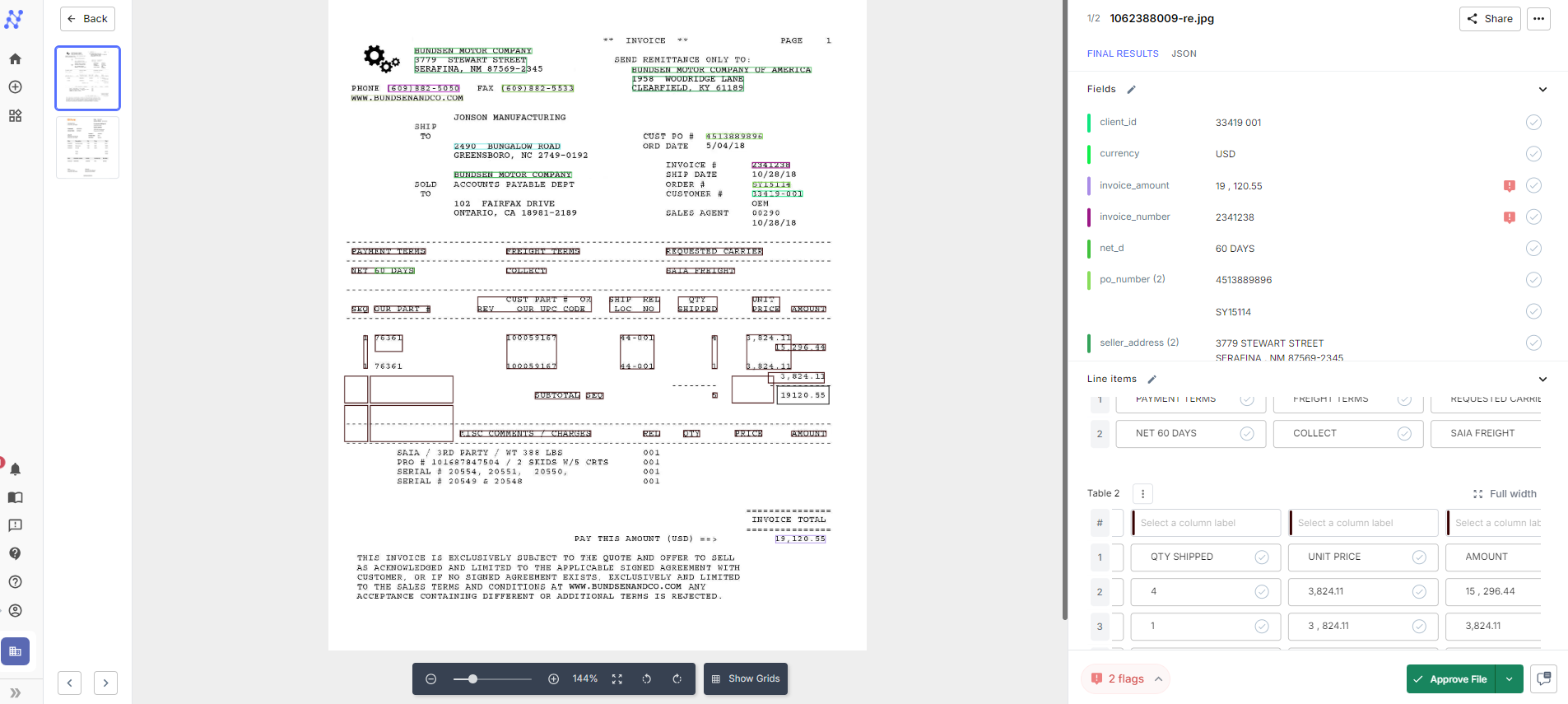
2. Inability to handle diverse document formats and layouts
AP departments receive various vendors' invoices, purchase orders, and receipts in multiple formats and layouts. Traditional OCR systems often require manual template creation for each new format, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Moreover, these documents can also have variations within the same format, such as different line item structures, subtotal placements, or payment terms. This diversity poses a significant challenge for traditional OCR systems.
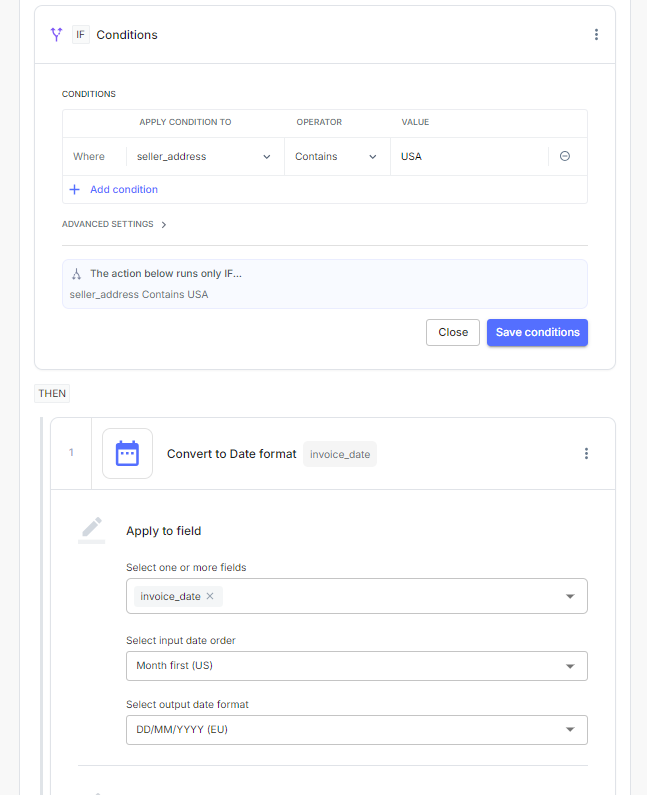
3. Limited understanding of unstructured data and context
Traditional OCR technology can extract text from documents but may not understand the context or meaning behind the data. This limitation can cause errors in data interpretation, particularly for unstructured information like line-item descriptions or payment terms, requiring further manual validation.
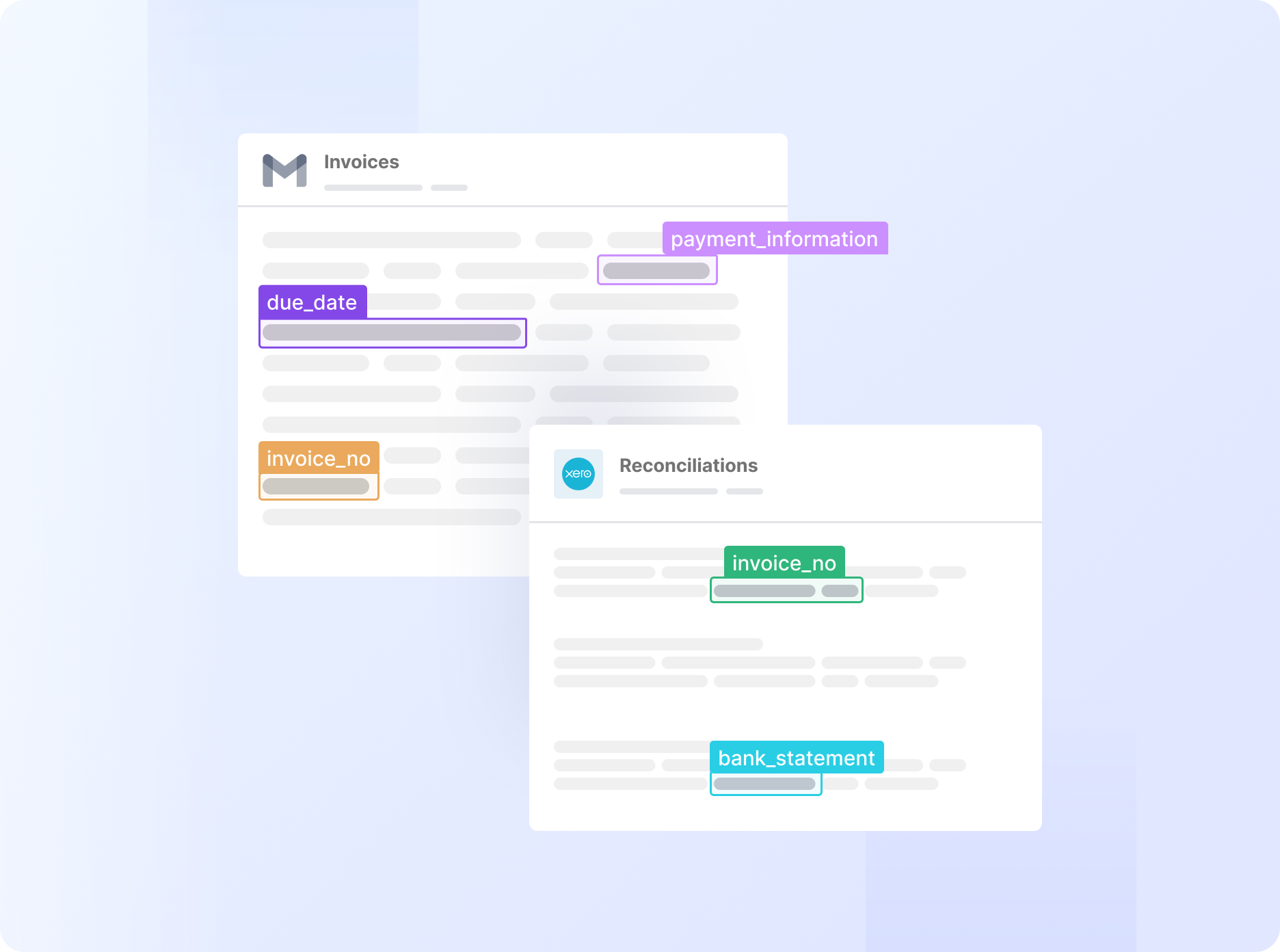
4. Difficulty in automating invoice workflows
Traditional OCR solutions may integrate well with your accounting tools and ERPs, but they may not be able to run fully automated end-to-end invoice processing workflows. For instance, they may not be able to automatically map the data extracted from invoices to the corresponding fields in your ERP or accounting system.
This happens because traditional OCR solutions are designed to extract text from invoices but lack the intelligence to interpret the meaning of the data and match it to the correct fields in your ERP. As a result, your AP team still needs to manually review the extracted data and enter it into the correct fields in your ERP, negating much of the automation benefit.

5. Limited options for file ingestion and invoice capture
Traditional OCR systems may have limited options for ingesting files and capturing invoices, often requiring manual scanning or uploading of documents. This can be time-consuming and hinder the automation of the AP process, particularly for organizations that receive invoices through multiple channels, such as email, paper, and electronic formats.
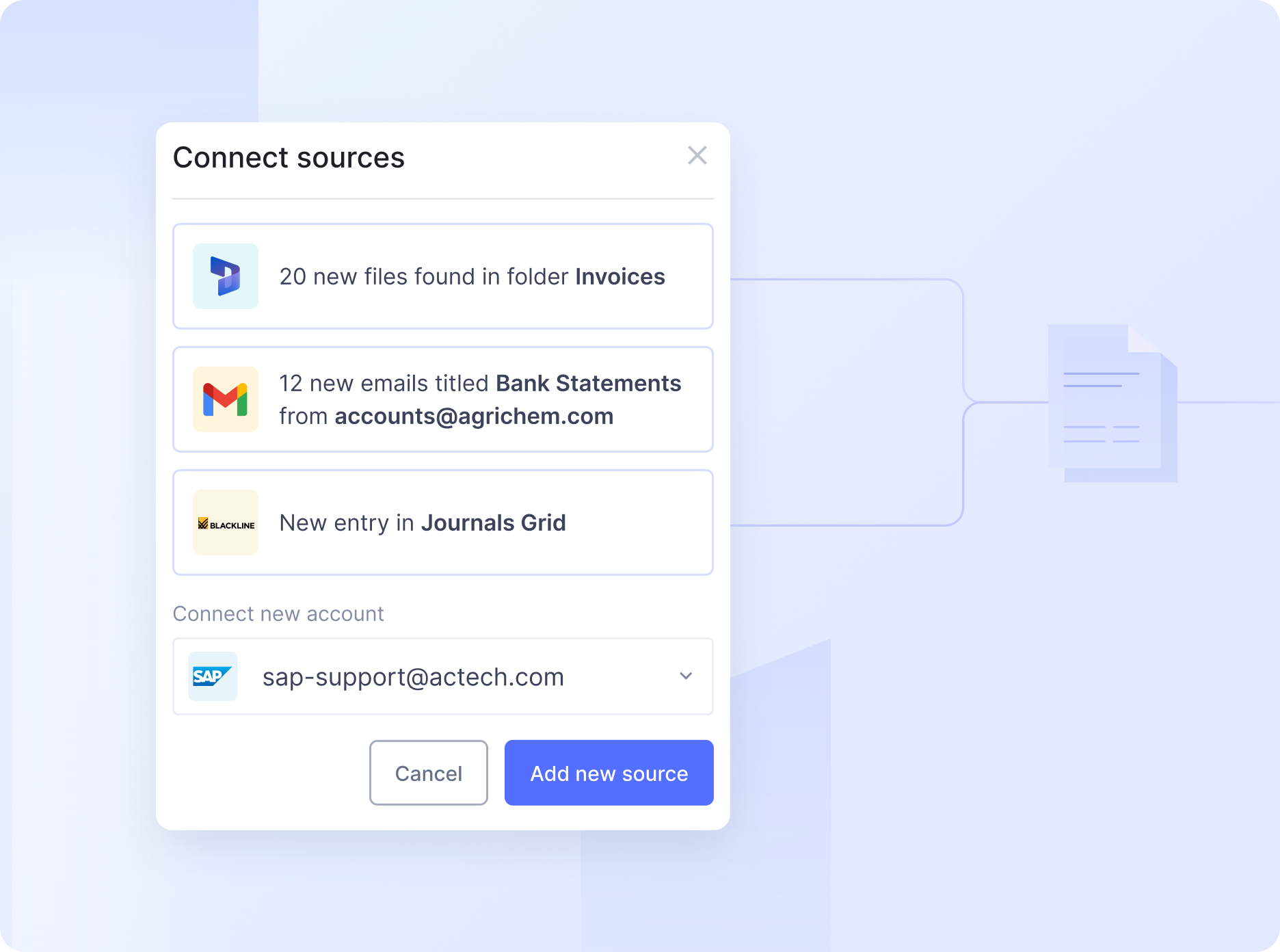
Adopting advanced OCR tools can help you successfully overcome the challenges associated with traditional OCR technology. These cutting-edge solutions enable businesses to achieve higher accuracy, efficiency, and scalability in their accounts payable processes, leading to cost savings and improved financial control.
Final thoughts
As the business landscape evolves and digital transformation becomes increasingly critical, embracing OCR and AP automation will be vital to staying competitive and agile. Investing in the right solutions, processes, and people will allow you to position yourselves for long-term success and unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation in the years ahead.
If you're ready to take the first step towards automating your AP processes with OCR, Nanonets can help. Our AI-powered OCR solution is designed to streamline your invoice processing from end to end with advanced features like automated data extraction, validation, and integration with your existing systems.
Schedule a demo today to see how Nanonets can help you invoice OCR and AP automation.
