Financial & accounting documents play a critical role in driving business processes. Businesses handle & verify various financial or accounting documents such as invoices, customer orders, receipts or purchase orders as part of their daily workflows. And as businesses grow they have to handle & process a lot of such financial documents.
Organizations tend to have dedicated accounting teams (or outsourced AP teams) to check financial documents, enter the data into accounting software, verify the data against supporting documentation, and finally process transactions if needed.
For example, an organization might need to verify a supplier’s invoice against a purchase order (PO) it had placed, before approving/processing the invoice; this would entail a verification process that matches each line item on the invoice with a corresponding entry in the PO - in other words an end-to-end accounts payable process.
Such elaborate interventions & verifications are mandated by regulatory and ethical requirements. And these are often carried out manually because the various accounting & financial documents are not always machine readable!
Often shared as scans, PDFs or paper, these documents require substantial manual efforts to enter the digital workflows that power businesses today. These manual interventions by finance & accounting personnel tend to be time consuming & error prone (at scale), taking up resources that could be put to better use.
And that’s where OCR, or Optical Character Recognition, can help! (What is OCR? And what is it used for? For a detailed explainer on OCR and its use cases refer this guide.)
OCR in Finance & Accounting
OCR finance or OCR accounting refers to the application of OCR technology to automate the extraction of financial/accounting data from documents - also referred to as financial spreading or accounting cycle automation.
OCR tools can automatically recognize & extract text, characters, fields or data from scanned documents & images. And since the documents in question mostly present structured data across standard formats, automated OCR finance or OCR accounting could greatly reduce processing times for each document.
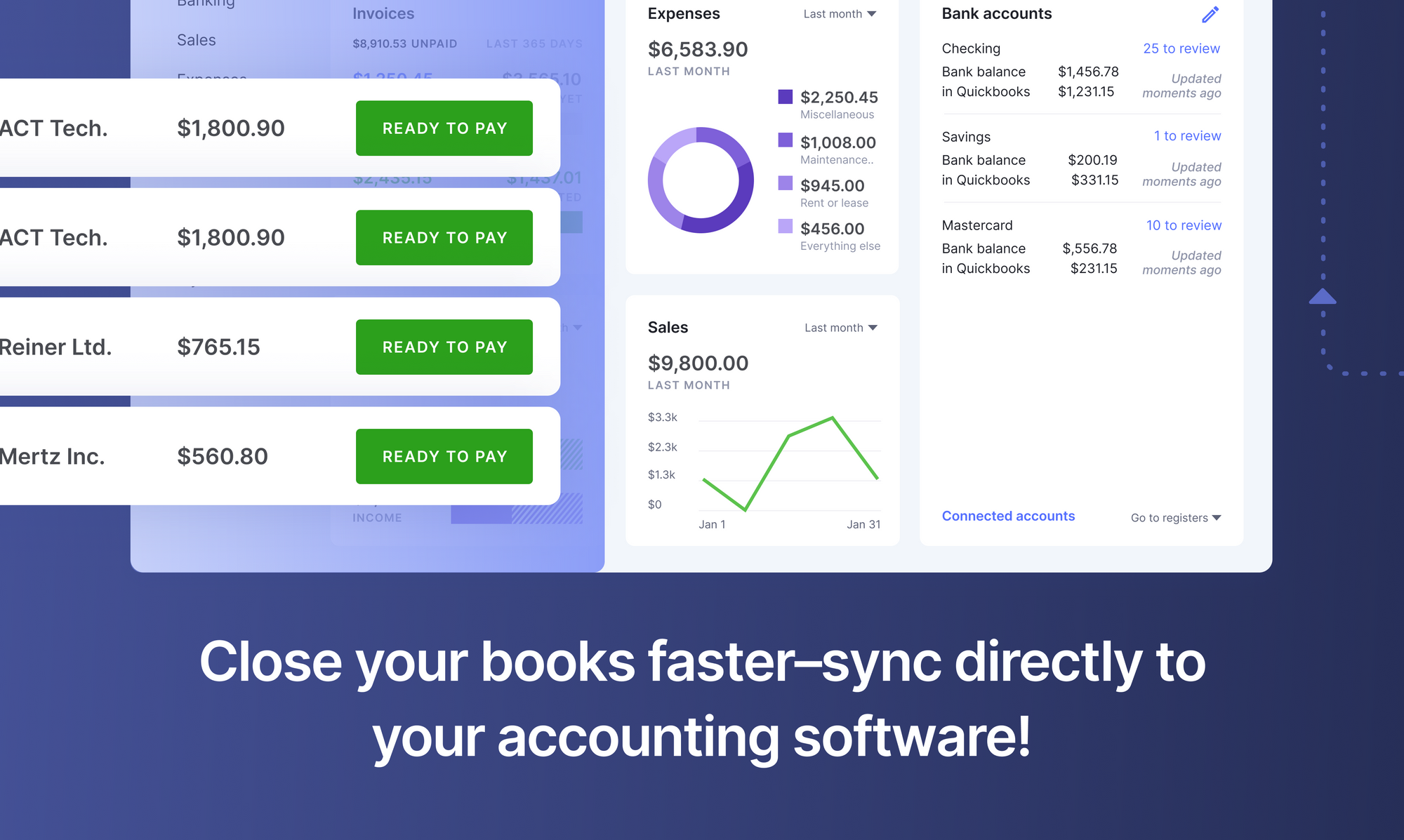
For example, an OCR system could extract & present fields (or line items) of interest from related POs, invoices & receipts so that accounting teams can do a quick & efficient 3-way match. Or PDF OCR software could convert bank PDF statements into Excel or CSV for easier downstream processing.
This avoids all the manual effort that would otherwise have been necessary to extract relevant data from these financial documents. Automated OCR software, a key tool in financial document automation, can thus seamlessly connect with accounting or ERP software to create a completely digital workflow.
OCR finance or OCR accounting automation applications allow financial analysts and accountants to focus on higher level, more technical or specialized, tasks that contribute more value to their organizations. OCR also introduces a greater level of accuracy and precision to routine tasks that would otherwise have been carried out manually.
Benefits of OCR Finance & OCR Accounting Applications
Analysts & accountants are increasingly leveraging OCR to shift their focus & time from data entry to data review; this improves overall employee efficiency & productivity. Implementing OCR solutions therefore brings its own share of unique benefits:
- Reduce cost - Reduce operational costs by eliminating the inefficient processes of manual data entry and verification. Eliminate related document storage and processing costs.
- Improve processing speed - Automated OCR accounting automation software can extract and verify data in minutes; a task that would otherwise have required many man-hours. OCR can help organizations reduce time spent on manual paperwork by over 75% or more.
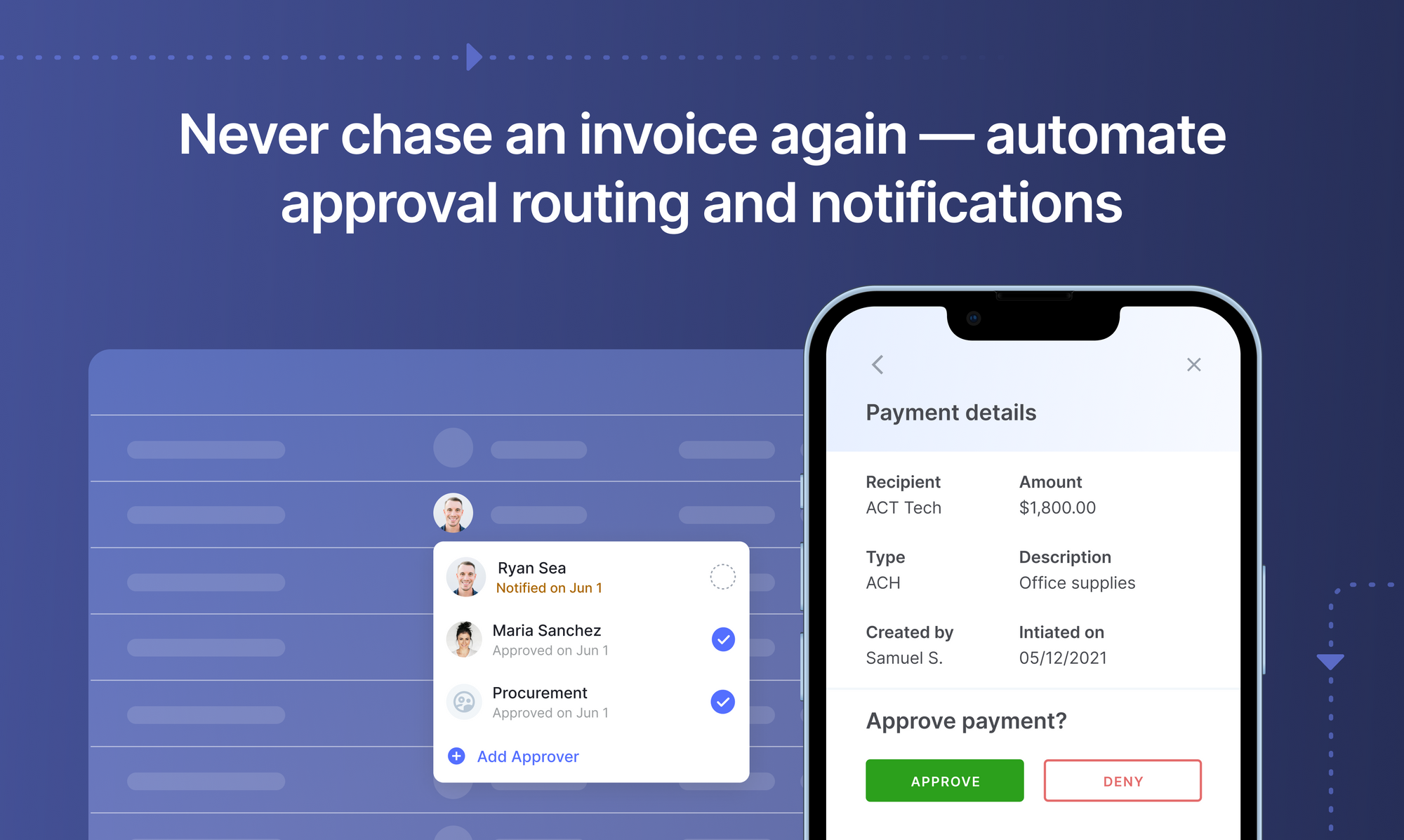
- Streamline payment processing - OCR finance & OCR accounting software (or AP automation software)can help automate or streamline accounts payable (AP), accounts receivable (AR) & check processing among other internal payment processes.
- Process documents intelligently - AI-based OCR software like Nanonets, can classify specific document types from a mixed bunch regardless of the format. Even if presented with a bunch of “unknown” documents, automated OCR software can intelligently classify documents by type (invoice, receipt, bill etc.) or source (supplier, vendor, internal etc.) for further processing & data extraction.
- Improve data accuracy - OCR software leverage AI algorithms & ML capabilities to offer a high degree of accuracy while extracting data from documents. Better accuracy leads to reduced errors and rework which ultimately saves time and money!
- Scale easily - Automated OCR finance software can handle very high volumes of documents quite easily.
- Save the environment - Organizations can reduce the use of paper documents or go paperless as OCR can handle digital document formats.
- Keep employees motivated - Manual processes and paperwork can be extremely boring, especially for accountants & financial analysts. Organizations that adopt OCR use cases, can turn their workforce towards more challenging or engaging tasks.
Set up touchless AP workflows and streamline the Accounts Payable process in seconds. Book a 30-min live demo now.
OCR Finance & OCR Accounting Use Cases
OCR finance & OCR accounting have many interesting use cases with respect to AI document processing workflows. Since accounting & financial documents mostly deal with structured data presented in standardized formats, OCR can handle pretty much any document related to these disciplines.
The most common OCR use cases for financial documents are invoice OCR (also known as invoice scanning & automated invoice processing) & receipt OCR. Extracting relevant fields of data from invoices or receipts can help organizations process transactions more quickly, avoiding delays and potential fines. These OCR use cases typically fall under the category of AP automation, spend management software or expense management.
Here’s a case-study on how Minnesota’s largest construction company improved its AP productivity with OCR finance.
The Nanonets Receipt OCR in action
Banking use cases would include processing various applications (for loans, new accounts or check requests) or doing KYC verifications. OCR software can scan application forms, extract relevant fields & populate the same in banking software for faster processing. ID card OCR or identity OCR currently powers most of the mobile-based KYC processes offered by modern banks. These OCR use cases allow banks to fast-track processes that could turn into potential customer pain points. Here’s another case-study on how a KYC platform leveraged OCR to process more than 50,000 Drivers licenses per month.
Insurance companies can similarly automate claims processing with the aid of OCR technology. Insurance OCR can expedite claims verification and claims processing, benefiting consumers and insurance companies alike. Apart from processing insurance-related documents, OCR can also be used to assess physical damage related to insurance claims.
OCR can also be used to simplify accounting related processes by integrating with accounting software. Here’s an interesting case-study on how a business used OCR software to simplify accounting processes related to QuickBooks.
Businesses also use accounting OCR for improving audits and reports on expenses. OCR tools compare and match various document trails to help accountants flag fraudulent charges and business expenses. Here are some examples of potential fraudulent charges that businesses might encounter: blank receipts for non-business transactions, duplicate expense receipts, inflated invoices, or amount mismatches.
Nanonets OCR
Nanonets Intro
Nanonets is an AI-based OCR software that is easy to set up and use, offering convenient pre-trained models for popular financial OCR & accounting OCR use cases. Extract financial/accounting data in seconds or train a custom deep learning OCR model to meet your specific data extraction needs.
Train your Own Invoice Model with Nanonets
The advantages of using Nanonets over other OCR software parsers (like Power Automate) go far beyond just better financial automation, accuracy & AI/ML capabilities. Here are some of the unique Nanonets benefits:
- Nanonets OCR isn't template-based. Apart from offering pre-trained models for popular use cases, its intelligent document processing algorithm can also handle unseen document types!
- Nanonets handles unstructured data, common data constraints, multi-page documents, tables and multi-line items with ease.
- Nanonets is a no-code intelligent automation platform that can continuously re-train itself and [learn] from custom data sets. Outputs require almost no post-processing.
- Every aspect of [document processing] can be customized with Nanonets. Right from document recognition & data extraction to output styles and formats!
- Nanonets was built for hassle-free integration, even with legacy systems. You can also easily integrate Nanonets with most CRM, ERP or [RPA] software.
Nanonets Documentation
If you’re looking to train your own OCR finance or OCR accounting models, check out the Nanonets API. In the documentation, you will find ready-to-fire code samples in Shell, Ruby, Golang, Java, C#, and Python, as well as detailed API specs for different endpoints.
Book this 30-min live demo to make this the last time that you'll ever have to manually key in data from invoices or receipts into ERP software.
Update Nov 2022: this post was originally published in March 2020 and has since been updated.
Here's a slide summarizing the findings in this article. Here's an alternate version of this post.
Frequently asked questions
1. How do I implement OCR for automated invoice processing?
Implementing OCR for automated invoice processing requires a systematic approach that starts with selecting the right OCR platform and configuring it for your specific invoice formats:
Step 1: Platform Selection and Setup
• Choose an AI-powered OCR solution like Nanonets that supports intelligent document processing rather than template-based systems
• Configure automated data import from various sources including email, FTP, cloud storage, and direct uploads
• Set up user accounts and access permissions for your accounts payable team
Step 2: Document Classification and Field Mapping
• Train the system to recognize different invoice formats from various vendors automatically
• Define key data fields for extraction: vendor information, invoice numbers, dates, line items, totals, tax amounts
• Configure validation rules for critical fields like purchase order matching and duplicate detection
Step 3: Workflow Integration
• Connect OCR output to your existing ERP or accounting systems through APIs
• Establish approval workflows that route invoices based on amount thresholds, vendor types, or department codes
• Set up exception handling processes for invoices that require manual review due to discrepancies or low confidence scores
Step 4: Quality Control and Optimization
• Implement confidence score thresholds to ensure only high-quality extractions proceed automatically
• Create feedback loops for continuous model improvement based on user corrections
• Monitor processing metrics and adjust settings to optimize accuracy and throughput rates
2. What cost savings can I expect from implementing OCR in finance?
OCR implementation in finance delivers substantial cost savings across multiple operational dimensions with measurable returns typically visible within 3-6 months:
Direct Labor Cost Reduction:
• Reduce manual data entry time by 75-90% for routine financial document processing
• Cut invoice processing costs from industry average of $12-15 per invoice to $2-4 per invoice
• Eliminate need for temporary staffing during peak processing periods
• Free up skilled accounting personnel for higher-value analytical and strategic tasks
Operational Efficiency Gains:
• Reduce document processing time from days or weeks to minutes or hours
• Achieve straight-through processing rates of 80-90% for standard documents versus 30-40% with manual processes
• Minimize late payment penalties through faster invoice processing and approval cycles
• Reduce audit preparation time by 60-80% through automated document organization and data validation
Error Reduction and Risk Mitigation:
• Cut data entry errors by 85-95% compared to manual processing
• Prevent duplicate payments through automated invoice matching and verification
• Reduce compliance violations and associated penalties through consistent data capture and documentation
• Minimize fraud losses through automated anomaly detection and validation checks
Scalability Benefits:
• Handle 300-500% more document volume without proportional staff increases
• Maintain consistent processing quality regardless of volume fluctuations
• Reduce storage costs by 70-80% through digital document management
• Lower overall operational costs while improving service levels and accuracy
3. How does OCR integrate with existing accounting and ERP systems?
OCR integration with accounting and ERP systems follows established patterns that ensure seamless data flow and maintain system integrity:
API-Based Integration Methods:
• REST APIs: Most modern OCR platforms provide RESTful APIs that connect directly to ERP systems like SAP, Oracle, or NetSuite
• Webhook notifications: Real-time data push to accounting systems immediately after document processing
• Batch processing: Scheduled data transfers for high-volume operations during off-peak hours
• Direct database connections: Secure database-to-database transfers for enterprise environments
Popular Integration Platforms:
• QuickBooks integration: One-click connections with pre-built field mapping for invoices, receipts, and expense reports
• Xero connectivity: Native integration supporting automatic transaction posting and reconciliation
• SAP modules: Dedicated connectors for Accounts Payable, Financial Accounting, and Materials Management
• Microsoft Dynamics: Built-in integration supporting multiple business processes and approval workflows
Data Transformation and Validation:
• Field mapping: Configure how OCR output fields correspond to ERP system fields
• Data validation: Implement business rules to verify extracted data before system posting
• Format conversion: Transform data into required formats (XML, JSON, CSV) for target systems
• Duplicate detection: Prevent duplicate entries through intelligent matching algorithms
Workflow Automation Features:
• Approval routing: Automatically route documents through predefined approval hierarchies
• Exception handling: Flag discrepancies for manual review while allowing clean documents to process automatically
• Audit trails: Maintain complete processing history for compliance and troubleshooting
• Real-time monitoring: Track processing status and system performance through integrated dashboards
4. What are the key differences between traditional OCR and AI-powered OCR for finance?
The distinction between traditional and AI-powered OCR represents a fundamental shift in document processing capabilities and business value:
Traditional OCR Limitations:
• Template dependency: Requires predefined templates for each document format, making it inflexible for varying layouts
• Limited context understanding: Processes text character-by-character without understanding document structure or meaning
• Manual configuration: Needs extensive setup and maintenance for each new document type or vendor
• Poor exception handling: Struggles with documents that deviate from established templates or contain unexpected elements
AI-Powered OCR Advantages:
• Adaptive processing: Uses machine learning to understand document structure and context automatically
• Intelligent field extraction: Recognizes data fields based on labels, positioning, and semantic meaning rather than fixed coordinates
• Continuous learning: Improves accuracy over time through user feedback and additional training data
• Format flexibility: Handles varying document layouts, fonts, and structures without requiring new templates
Financial Document Specific Benefits:
• Multi-vendor support: Processes invoices from hundreds of different vendors without individual template setup
• Complex table extraction: Accurately captures line items, taxes, and totals from varied table formats
• Relationship understanding: Recognizes connections between related fields (PO numbers with line items, taxes with subtotals)
• Anomaly detection: Identifies unusual patterns that may indicate errors or fraudulent activity
Implementation and Maintenance Differences:
• Setup time: AI-powered systems deploy in days versus weeks or months for traditional template-based systems
• Ongoing maintenance: Minimal intervention required versus constant template updates for traditional OCR
• Accuracy improvement: Self-improving accuracy through machine learning versus static performance in traditional systems
• Total cost of ownership: Lower long-term costs despite higher initial investment due to reduced maintenance requirements
5. How does OCR support regulatory compliance in financial services?
OCR technology plays a crucial role in meeting stringent regulatory requirements across various financial service sectors:
Documentation and Audit Trail Requirements:
• Complete processing records: OCR systems maintain detailed logs of all document processing activities, including timestamps, user actions, and confidence scores
• Data lineage tracking: Provides clear audit trails showing the source of extracted data and any manual modifications made during processing • Version control: Maintains historical records of document versions and processing iterations for regulatory review
• Automated compliance reporting: Generates standardized reports required by regulators using extracted and validated data
Data Quality and Accuracy Standards:
• Validation frameworks: Implement multi-level validation checks to ensure extracted data meets regulatory accuracy requirements
• Error detection and correction: Automated identification of data inconsistencies or missing information required by compliance standards
• Cross-reference verification: Compare extracted data against authoritative sources and flag discrepancies for review
• Quality metrics monitoring: Track and report on data accuracy rates to demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards
Privacy and Security Compliance:
• Data encryption: Ensure all extracted financial data is encrypted both in transit and at rest to meet privacy regulations
• Access controls: Implement role-based access to sensitive financial information with detailed activity logging
• Data retention policies: Automatically enforce document retention schedules required by regulations like SOX or Basel III
• Personal data protection: Identify and properly handle personally identifiable information according to GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy laws
Specific Regulatory Applications:
• KYC compliance: Automate customer identity verification by extracting data from government-issued IDs and supporting documents
• Anti-money laundering (AML): Process large volumes of transaction documents to identify suspicious patterns and reporting requirements
• Tax compliance: Ensure accurate extraction and reporting of tax-related information from various financial documents
6. What are the best practices for OCR data validation in finance?
Effective OCR data validation in finance requires multiple layers of verification to ensure accuracy and reliability:
Multi-Level Validation Framework:
• Technical validation: Verify data format consistency (dates, currencies, account numbers) and field completeness
• Business rule validation: Apply financial logic checks such as tax calculations, total reconciliation, and reasonable amount ranges
• Cross-document verification: Match extracted data against related documents like purchase orders, contracts, or previous transactions
• External data verification: Validate vendor information, tax IDs, and bank details against authoritative external databases
Automated Quality Control Measures:
• Confidence score thresholds: Set minimum confidence levels (typically 85-95%) for automatic processing approval
• Pattern recognition: Identify unusual patterns in extracted data that may indicate processing errors or fraudulent activity
• Mathematical validation: Verify calculations, totals, tax computations, and line item summations for accuracy
• Duplicate detection: Compare incoming documents against historical records to prevent duplicate processing
Exception Handling Workflows:
• Intelligent routing: Automatically direct documents with validation failures to appropriate reviewers based on error type and document value
• Review queues: Organize failed validations by priority, document type, and required expertise for efficient manual review
• Escalation procedures: Define clear escalation paths for complex validation issues or high-value discrepancies
• Feedback integration: Capture manual corrections and feed them back to improve future OCR accuracy
Continuous Improvement Processes:
• Performance monitoring: Track validation success rates, common error types, and processing times to identify improvement opportunities
• Model refinement: Use validation feedback to retrain and improve OCR models for better future performance
• Process optimization: Regularly review and update validation rules based on changing business requirements and regulatory standards
• User training: Ensure staff understand validation procedures and can effectively handle exceptions and edge cases
7. How do banks use OCR for customer onboarding and KYC processes?
Banks leverage OCR technology to streamline customer onboarding and meet Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements efficiently:
Identity Document Processing:
• Government ID extraction: Automatically capture data from driver's licenses, passports, and national identity cards including names, addresses, dates of birth, and ID numbers
• Document authentication: Verify security features, detect tampering, and confirm document validity through integrated verification systems
• Multi-format support: Process various document types and formats from different countries and jurisdictions
• Real-time processing: Enable instant customer verification during digital account opening processes
Address and Income Verification:
• Utility bill processing: Extract customer names, addresses, and service dates from utility bills to verify residence
• Bank statement analysis: Capture income information, account balances, and transaction patterns for creditworthiness assessment
• Pay stub digitization: Process employment documents to verify income sources and employment stability
• Tax document processing: Extract relevant financial information from tax returns and W-2 forms
Compliance and Risk Management:
• Sanctions screening: Automatically extract names and identification numbers for screening against regulatory watchlists
• PEP identification: Process documents to identify politically exposed persons and apply enhanced due diligence procedures
• Record keeping: Maintain digital copies of all processed documents with complete audit trails for regulatory compliance
• Quality assurance: Implement validation checks to ensure accuracy of extracted data and flag potential issues
Customer Experience Enhancement:
• Mobile onboarding: Enable customers to complete account opening using smartphone cameras to capture required documents
• Reduced processing time: Cut account opening time from days to minutes through automated document processing
• Error reduction: Minimize manual data entry errors that could delay account activation or cause compliance issues
• Multi-language support: Process documents in various languages to serve diverse customer populations effectively
8. How do I handle poor quality scanned financial documents with OCR?
Managing poor quality scanned documents requires a combination of preprocessing techniques, advanced OCR capabilities, and quality control measures:
Image Enhancement Preprocessing: • Resolution optimization: Upscale low-resolution images to minimum 300 DPI for optimal OCR performance • Deskewing and rotation: Automatically correct document orientation and straighten skewed or rotated images • Noise reduction: Apply filters to remove background noise, speckles, and artifacts that interfere with text recognition • Contrast enhancement: Improve text-to-background contrast through histogram equalization and adaptive thresholding
Advanced OCR Techniques: • AI-powered recognition: Use machine learning-based OCR that can better handle variations in font quality, size, and clarity • Multi-pass processing: Apply different OCR engines or settings to the same document and compare results for better accuracy • Contextual analysis: Leverage document understanding to infer missing or unclear characters based on surrounding text and document structure • Confidence scoring: Implement detailed confidence metrics to identify questionable extractions that require manual review
Quality Assessment and Routing: • Automated quality detection: Use algorithms to assess document quality and route poor-quality documents to specialized processing workflows • Human-in-the-loop workflows: Establish efficient review processes for documents that fall below quality thresholds • Progressive enhancement: Apply increasingly sophisticated processing techniques based on initial OCR success rates • Alternative capture methods: Provide options for re-scanning or alternative document submission when quality is insufficient
Fallback and Recovery Strategies: • Manual data entry backup: Maintain processes for manual extraction when OCR fails completely • Partial processing: Extract whatever data is readable and clearly identify missing or uncertain information • Customer communication: Establish protocols for requesting higher quality documents when processing fails • Quality improvement feedback: Use poor quality examples to improve preprocessing algorithms and OCR model training
9. What security measures are needed for OCR processing of sensitive financial data?
Protecting sensitive financial data during OCR processing requires comprehensive security measures across all system components:
Data Encryption and Protection: • End-to-end encryption: Encrypt all financial documents and extracted data both in transit and at rest using AES-256 or equivalent standards • Secure transmission: Use TLS 1.3 or higher for all API communications and document uploads • Encrypted storage: Store processed documents and extracted data in encrypted databases with proper key management • Secure deletion: Implement verified data destruction procedures for documents beyond retention periods
Access Control and Authentication: • Multi-factor authentication: Require strong authentication for all users accessing OCR systems and financial data • Role-based permissions: Implement granular access controls based on job functions and data sensitivity levels • Audit logging: Maintain detailed logs of all user activities, data access, and system operations • Session management: Enforce secure session policies with automatic timeouts and re-authentication requirements
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: • PCI DSS compliance: Meet payment card industry standards for handling credit card and payment information • SOX compliance: Implement controls and audit trails required for financial reporting accuracy and integrity • GDPR/privacy regulations: Ensure proper handling of personal financial information with consent management and data subject rights • Industry-specific requirements: Meet sector-specific regulations such as GLBA for financial institutions or HIPAA for healthcare finance
Operational Security Measures: • Network security: Deploy firewalls, intrusion detection, and network segmentation to protect OCR processing infrastructure • Vulnerability management: Regularly assess and patch security vulnerabilities in OCR software and supporting systems • Incident response: Establish procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security incidents • Vendor security: Evaluate and monitor security practices of third-party OCR providers and ensure contractual security requirements • Data backup and recovery: Implement secure backup procedures with encrypted storage and tested recovery processes