Month-End Reconciliation: How Tos, Best Practices and More
The end of each month marks a crucial period for businesses. It's when tallying financial records for accuracy and completeness becomes paramount. Month-end reconciliation, also known as month-end closing or month-end financial close, is a fundamental process that ensures the accuracy of financial data and sets the stage for informed spending and decision-making.
In this article, we'll define and cover the significance of month-end reconciliation, exploring best practices, common challenges, and how advanced automation tools like Nanonets can increase your business’ efficiency with this accounting practice. Whether you're a seasoned financial professional or new to the world of accounting, understanding the ins and outs of end of month reconciliation is essential for maintaining financial integrity and achieving business outcomes.
What is Month-End Reconciliation?
Month-End Reconciliation
Ensure the accuracy and completeness of financial records.
1. Consolidate Financial Data
Collect data from bank statements, invoices, receipts, and general ledger entries.
2. Review and Cross-Check Records
Meticulously review and cross-check records to identify discrepancies or errors.
3. Achieve Consistency
Ensure internal financial records align with external documents like bank statements and vendor invoices.
4. Identify and Correct Discrepancies
Identify any discrepancies, errors, or irregularities and take corrective actions.
5. Key Reconciliation Steps
- Review bank balances
- Verify account balances
- Reconcile accounts receivable and accounts payable
- Adjust discrepancies
6. Prepare Financial Statements
Prepare financial statements and reports for internal and external stakeholders.
Month-end reconciliation is an accounting process performed at the close of each month to ensure the accuracy and completeness of financial records. It involves comparing and verifying various financial transactions, accounts, and balances to ensure they align with expected values and are in line with established accounting standards.
At the heart of month-end reconciliation lies the consolidation of financial data from various sources, such as bank statements, invoices, receipts, and general ledger entries. These records are meticulously reviewed and cross-checked to identify any discrepancies or errors that may have occurred during the month.
The primary objective of month-end reconciliation is to achieve consistency between internal financial records and external documents, such as bank statements and vendor invoices. By reconciling these records, businesses can identify any discrepancies, errors, or irregularities and take corrective actions to ensure the accuracy of their financial reports.
Month-end reconciliation typically involves several key steps, including the review of bank balances, verification of account balances, reconciliation of accounts receivable and accounts payable, and adjustment of any discrepancies found. Additionally, it may also include the preparation of financial statements and reports for internal and external stakeholders.
Overall, month-end reconciliation serves as a vital process for maintaining financial accuracy, compliance with regulatory requirements, and providing stakeholders with reliable financial information for decision-making purposes.
Significance of Monthly Reconciliation
Monthly reconciliation holds significant importance for businesses of all sizes and across various industries.
It is the end of month reconciliations that ensure the accuracy and integrity of financial records by identifying and rectifying any discrepancies or errors. This accuracy is crucial for making informed business decisions and maintaining financial health.
Many regulatory authorities require businesses to maintain accurate and up-to-date financial records. Monthly reconciliation helps businesses ensure compliance with these regulations and avoid potential penalties or legal issues.
Regular reconciliation helps detect errors, omissions, or fraudulent activities in financial transactions. By comparing different sets of financial data, businesses can identify inconsistencies and take corrective actions promptly.
Accurate financial data resulting from monthly reconciliation provides business leaders and stakeholders with reliable information for decision-making purposes. It enables them to assess the financial health of the company, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic decisions accordingly.
The process of monthly reconciliation also promotes transparency and accountability within the organisation, ensuring that financial transactions are properly recorded and documented. It creates trust among employees, investors, creditors, as well as regulators.
Overall, monthly reconciliation plays a vital role in ensuring the financial integrity, compliance, and transparency of businesses, making it an essential practice for financial management.
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing Month-End Reconciliations
Performing month-end reconciliations is a crucial process to ensure the accuracy and completeness of financial records. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you navigate through the month-end reconciliation process:
- Gather Financial Statements: Start by gathering all relevant financial statements and documents for the month. This includes bank statements, credit card statements, invoices, receipts, and any other financial records.
- Review Transactions: Carefully review all transactions recorded during the month. This involves comparing entries in your accounting system with supporting documentation to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Match Transactions: Match transactions in your accounting system with corresponding entries in your bank and credit card statements. Ensure that all deposits, withdrawals, purchases, and payments are accurately recorded and accounted for.
- Identify Discrepancies: In case of any discrepancies or errors, investigate and resolve them promptly. This may involve contacting vendors or financial institutions to clarify transactions, correcting data entry errors, or updating records as necessary.
- Reconcile Bank Accounts: Reconcile your bank accounts by comparing the ending balances in your accounting system with the balances reported on your bank statements. Adjustments may be required to account for outstanding checks, deposits in transit, bank fees, and other factors.
- Review Balance Sheet Accounts: Review balance sheet accounts such as accounts receivable, accounts payable, and inventory to ensure that they are accurately recorded and reflect the correct balances at the end of the month.
- Perform Accruals and Adjustments: Make any necessary accruals and adjustments to ensure that revenue and expenses are recognized in the appropriate accounting period. This may include accruals for unbilled revenue, prepaid expenses, depreciation, and other adjustments.
- Document the Reconciliation Process: Document all steps taken during the month-end reconciliation process, including any adjustments made, discrepancies identified, and resolutions implemented. This documentation serves as a record of the reconciliation process and provides transparency for audit purposes.
- Finalise and Close the Month: Once all reconciliations and adjustments are completed, finalise the month-end financial statements and close the accounting period. This involves updating financial reports, generating month-end reports, and preparing for the next accounting period.
- Review and Audit: Finally, review the reconciled financial statements and reports for accuracy and completeness. Conduct internal audits or reviews to ensure compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements.
By following these step-by-step guidelines, you can effectively perform month-end reconciliations and ensure the accuracy and integrity of your financial records.
Challenges in Month-End Reconciliations
While month-end reconciliations are essential for maintaining accurate financial records, they also present several challenges that need to be mitigated beforehand.
Performing month-end reconciliations within a limited timeframe can be challenging, especially for businesses with large volumes of transactions. The process requires thorough review and analysis of financial data, which tends to be time-consuming. If rushed or done inefficiently, there may be errors, chaos, and undue delays.
Ensuring the accuracy of financial data is critical for month-end reconciliations. However, data entry errors, incomplete records, and discrepancies between different sources of data can pose challenges to the reconciliation process. Identifying and correcting these errors requires careful attention to detail and may require additional time and resources.
As businesses grow and expand, the complexity of financial transactions can increase, making month-end reconciliations more challenging. Complex transactions such as foreign currency transactions, intercompany transactions, and complex accounting entries require specialised knowledge and expertise to reconcile accurately.
Limited resources, including staff, time, and technology, can hinder the month-end reconciliation process. Businesses may struggle to allocate sufficient resources to perform reconciliations effectively, resulting in delays, errors, and inaccuracies in financial reporting.
Regulatory compliance and meeting accounting standards adds another layer of complexity to month-end reconciliations. Businesses must ensure that their reconciliations comply with relevant regulations and standards, which may require additional time and expertise.
Lastly, many businesses still rely on manual processes for month-end reconciliations, such as spreadsheets and manual data entry. While these methods may have been sufficient in the past, they are prone to errors and inefficiencies, especially as transaction volumes increase. Automating the reconciliation process can help mitigate these challenges and improve accuracy and efficiency. In the next section, we cover how best to do that.
Addressing these challenges requires proactive measures, including the implementation of automation tools, the adoption of best practices, and the allocation of adequate resources to the reconciliation process. By overcoming these challenges, businesses can ensure the accuracy and integrity of their financial records and make informed business decisions based on reliable data.
Best Practices for Month-End Reconciliations
Given the complexity of the end of month reconciliations, and the transaction volumes that some businesses have to handle, there are certain procedures that can help make the process smooth for all parties involved.
- Establish Clear Processes and Procedures: Define clear processes and procedures for month-end reconciliations, including roles and responsibilities, deadlines, and approval workflows. Having standardised processes in place ensures consistency and reduces the risk of errors and discrepancies.
- Utilise Automation Tools: Leverage automation tools to automate repetitive tasks and streamline the reconciliation process. Automation can help reduce manual errors, save time, and improve efficiency by automatically matching transactions, identifying discrepancies, and generating reports.
- Perform Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of financial data throughout the month to identify and address any discrepancies or issues early on. Regular reviews can help prevent errors from accumulating and ensure that financial records are accurate and up to date.
- Implement Segregation of Duties: Implement segregation of duties to ensure that no single individual has control over all aspects of the reconciliation process. Segregation of duties helps prevent fraud and errors by requiring multiple individuals to review and approve transactions.
- Maintain Documentation: Keep detailed documentation of the reconciliation process, including supporting documents, audit trails, and explanations for any adjustments or discrepancies. Documentation provides a clear audit trail and helps ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Conduct Regular Training: Provide regular training and education to staff involved in the reconciliation process to ensure they understand their roles and responsibilities and are familiar with best practices and procedures.
By following these best practices, businesses can improve the efficiency and accuracy of their month-end reconciliation process, reduce the risk of errors and discrepancies, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Month End Reconciliation Checklist
A month-end reconciliation checklist serves as a helpful tool to ensure that all necessary steps are completed accurately and efficiently. While specific requirements may vary depending on the nature and complexity of the business, the following checklist outlines essential tasks to include in the month-end reconciliation process:
- Review Bank Statements: Begin by reviewing bank statements to reconcile cash balances and ensure that all transactions are accurately recorded in the financial records.
- Match Transactions: Match transactions between bank statements and internal ledgers, ensuring that deposits, withdrawals, and other transactions are accurately reflected in both sets of records.
- Reconcile Accounts Receivable: Review accounts receivable balances to ensure that outstanding invoices are properly recorded and follow up on any overdue payments.
- Reconcile Accounts Payable: Review accounts payable balances to ensure that all outstanding invoices are accurately recorded and schedule payments for any outstanding bills.
- Review General Ledger: Conduct a thorough review of the general ledger to ensure that all accounts are properly reconciled and that all transactions are accurately recorded.
- Verify Revenue and Expenses: Verify revenue and expense transactions to ensure that they are properly recorded and classified in the correct accounts.
- Perform Accruals and Adjustments: Make any necessary accruals and adjustments to ensure that financial statements accurately reflect the financial position of the business.
- Review Financial Statements: Review financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Document Reconciliation Process: Document the reconciliation process, including any adjustments or corrections made, to provide a clear audit trail for future reference.
- Obtain Management Approval: Obtain management approval for the month-end reconciliation process to ensure accountability and oversight.
By following this month-end reconciliation checklist, businesses can ensure that their financial records are accurate, complete, and compliant with regulatory requirements. Additionally, documenting the reconciliation process provides transparency and accountability, helping to facilitate a smooth audit process and ensure the integrity of the financial reporting process.
How Nanonets Solves Month-End Reconciliations
Nanonets offers advanced automation solutions, with an AI/ML-enabled Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology, that streamlines the month-end reconciliation process and improves accuracy and efficiency.
With Nanonets, businesses can:
- Automate Data Extraction: Nanonets automates the extraction of financial data from various sources, including bank statements, invoices, and receipts. By eliminating manual data entry, Nanonets reduces the risk of errors and saves time.
- Match Transactions Automatically: Nanonets uses advanced matching algorithms to automatically match transactions between different sources, such as bank statements and internal ledgers. This helps identify discrepancies and inconsistencies quickly and accurately.
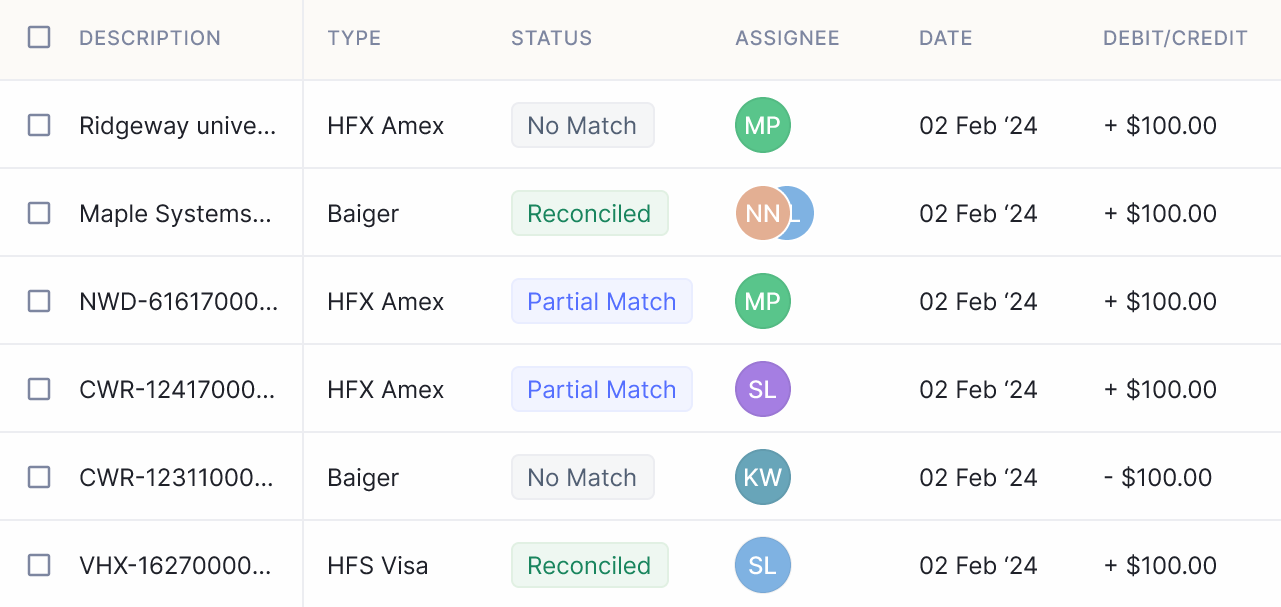
- Generate Reports Instantly: Nanonets generates comprehensive reports with detailed insights into the reconciliation process, including matched transactions, discrepancies, and adjustments. These reports provide valuable insights for decision-making and compliance purposes.
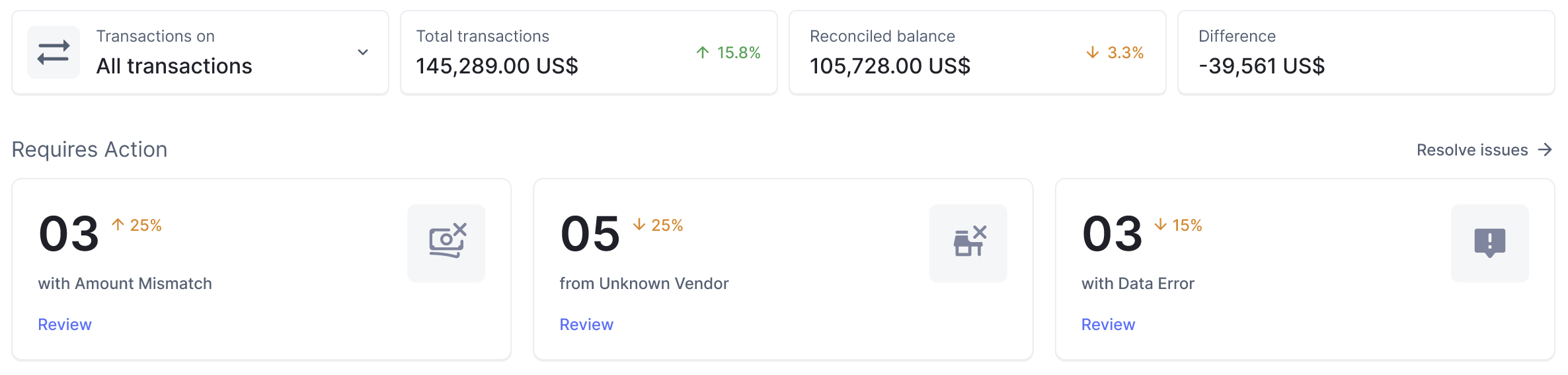
- Ensure Regulatory Compliance: Nanonets ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and accounting standards by providing audit trails, documentation, and transparency throughout the reconciliation process. This helps businesses maintain compliance and reduce the risk of penalties and fines.
- Improve Efficiency: By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining the reconciliation process, Nanonets improves efficiency and saves time and resources. This allows businesses to focus on more strategic activities and decision-making.
Overall, Nanonets empowers businesses to streamline their month-end reconciliation process, improve accuracy and efficiency, and make informed decisions based on reliable financial data.
Looking out for a Reconciliation Software?
Check out Nanonets Reconciliation where you can easily integrate Nanonets with your existing tools to instantly match your books and identify discrepancies.
Conclusion
The end of month reconciliation is a critical process for every business to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and integrity of a company's financial records. By reconciling accounts, verifying transactions, and reviewing financial statements at the end of each month, businesses can identify and address discrepancies, mitigate risks, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
Effective month-end reconciliation requires careful attention to detail, thorough documentation, and adherence to best practices. Utilising automation tools like Nanonets can streamline the reconciliation process, improve efficiency, and reduce the risk of errors.
By further following best practices, implementing efficient processes, and leveraging automation technology, businesses can optimise their month-end reconciliation process, gain valuable insights into their financial performance, and make informed decisions to drive success and growth.
In conclusion, month-end reconciliation is not just a routine task—it is a vital part of financial management that helps businesses maintain financial health, enhance decision-making, and achieve their strategic objectives.



