
Business data & transactions are increasingly going digital these days. And paper documents are being replaced with scanned images, PDFs, emails, and other digital formats. Business workflows run smoother on digital documents, as important data can be shared almost instantly.
The effect of this digital transformation can largely be seen in the way businesses process & validate invoices, using invoice scanners (also receipt scanners). As invoices, receipts, and POs are some of the most common documents that businesses have to process regularly.
What is an Invoice Scanner or Invoice Scanning?
An invoice scanner is a software that captures all the important data on invoices, presenting it in a machine readable format. It facilitates the seamless transfer of data in automated workflows.
Invoice scanning refers to the process of capturing and extracting invoice data (vendor, date, amount, invoice number, barcode, QR code etc.) for downstream business processes.
Looking to automate your manual AP Processes? Book a 30-min live demo to see how Nanonets can help your team implement end-to-end AP automation.
Why Use Invoice Scanning Software?
While digitized invoices can be shared easily, the data they carry is not readily accessible for downstream business processes. Invoices shared as PDFs or scanned images can’t be fed seamlessly into accounting or ERP software.
Not-editable formats such as PDFs or scanned documents are not machine readable. This poses a major challenge to organizations embracing digital transformation.
- So how can organizations access the neatly structured data trapped in scanned invoices?
- How can businesses digitally validate transactions shared as scanned invoices?
- How can accountants or data analysts extract important invoice data to ensure seamless workflows?
And that’s where invoice scanners or invoice scanning software come in handy!
Invoice scanning software (or invoice capture software) can recognize, extract & present key invoice data in a machine-readable format such as csv, Excel, JSON etc. By leveraging invoice scanners, businesses can ensure seamless digital workflows by feeding important invoice data wherever required.
How Automated Invoice Scanners Work
Invoice scanners employ OCR technology to extract information from digitized invoices. OCR, or Optical Character Recognition, allows invoice scanning software to recognize and then perform data capture. Here’s a detailed guide on OCR & its various use cases.
By leveraging AI & ML capabilities along with OCR, invoice scanners can be “trained” to only extract “key value pairs” of interest. Such automated invoice processing software can work “right out of the box” with pre-trained invoice scanning algorithms. Here’s a typical workflow:
- Upload invoices into the invoice scanner
- The invoice scanner then extracts relevant data according to your business rules
- The data is then presented as a machine readable structured output (CSV, JSON, DOC)
- This can then be fed into ERP software for other processes
Advanced invoice automation tools like Nanonets even allow users to build/train custom invoice scanning OCR models. Here are the general steps to train or build a custom invoice OCR:
- Upload sample invoices to serve as a training set
- “Teach” the algorithm by marking or annotating key invoice data fields on the training set
- Train the invoice scanner based on your custom inputs
- Test & verify the custom invoice scanner on real invoices
- If the output is satisfactory, your custom invoice scanner is ready
- If not, then repeat the process with more sample invoices in the training set
The Nanonets Invoice Scanner in action: pre-trained & custom variants
Set up touchless AP workflows and streamline the Accounts Payable process in seconds. Book a 30-min live demo now.
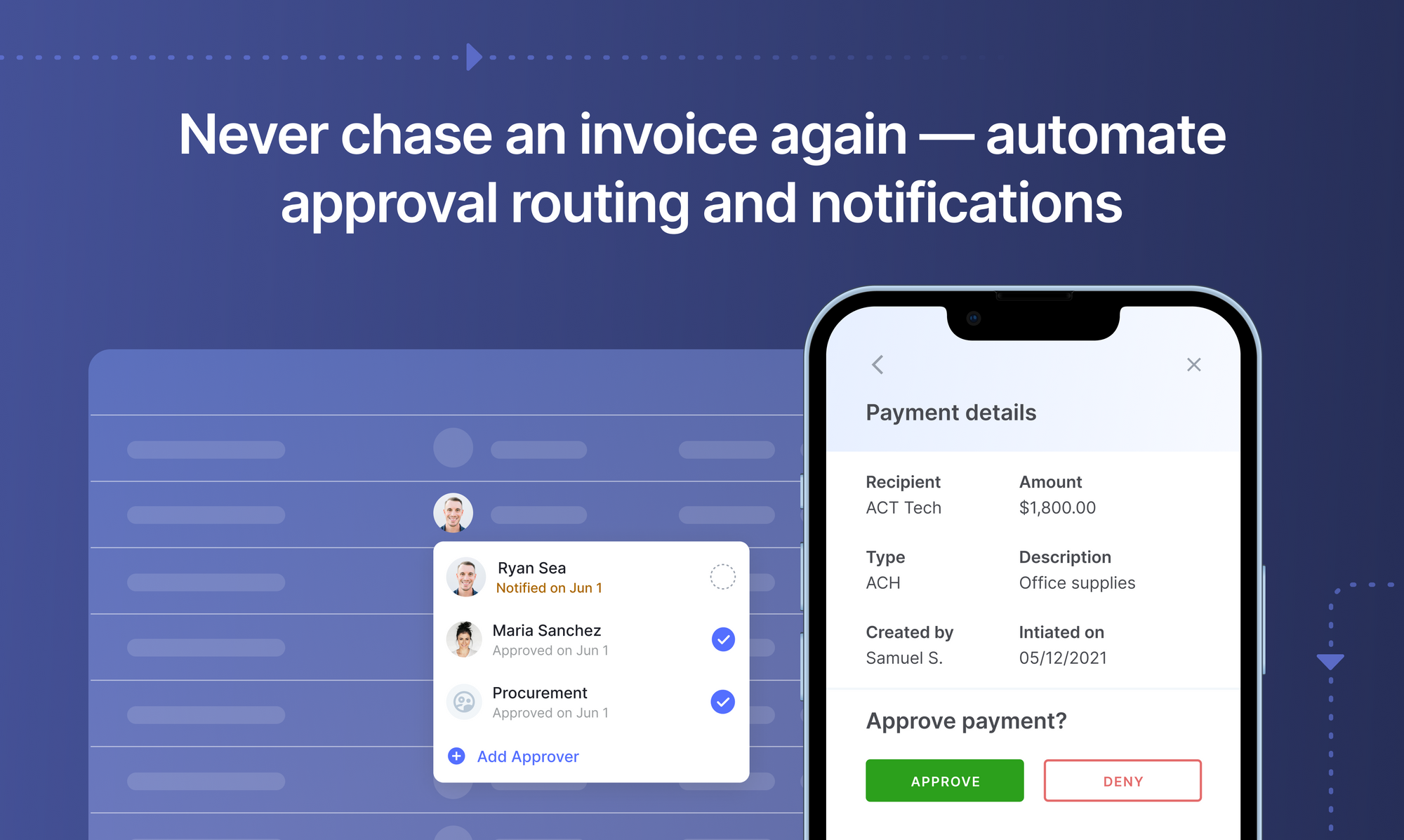
Benefits and Limitations of Automated Invoice Scanning
Like any other business solution, automated invoice scanning has its fair share of benefits & limitations. Weighing these could help businesses judge the viability of invoice scanning for internal processes.
Benefits:
- Higher accuracy and speed in comparison to manual processes, and fewer errors
- Apart from extracting invoice metadata (vendor, date, amount, invoice number etc.), automated invoice scanning can also extract invoice data from line items
- Reduced invoice processing time - from days to mere minutes - that could lead to early payment discounts
- Cost savings on account of eliminating inefficient manual processes & labor
- AP teams can devote precious man-hours towards more business-critical tasks
- A highly scalable process that can quickly accommodate higher volumes of data
- Integrates with ERP software to create an end-to-end digital workflow
- For example Nanonets’ invoice automation solution can integrate with QuickBooks & FreshBooks. Nanonets can also integrate with many more online apps & services.
- Can automate verifications like 3-way matching by extracting data from receipts & POs.
Limitations:
- Accuracy isn’t 100%
- Common data constraints such as handwritten text, blurred/unclear scans, low resolution images, unrecognizable/illegible fonts, and tilted text among others can affect overall performance & accuracy
- Doesn’t recognize unknown invoice formats
- Can’t capturing unstructured data
- Extracting data from tables & line items invoices is suboptimal
Advancements in Modern Invoice Scanning
The limitations highlighted above apply to most legacy invoice OCR tools & even to many automated invoice scanning solutions. But modern invoice automation tools, like Nanonets, have leveraged AI & ML capabilities to greatly reduce the effect, if not eliminate, these serious limitations.
- To tackle deficiencies in accuracy, modern invoice scanners employ algorithms that learn continuously. These invoice scanning algorithms retrain themselves regularly with new data that passes through the workflows.
- Modern invoice scanners aren’t template-based. These intelligent document processing tools that can “learn” to perform more accurately.
- Advanced Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning & Deep Learning techniques allow modern invoice scanning software to work on limited data. This allows them to handle common data constraints, unknown documents & unstructured invoice data with ease.
- Extracting tabular data and finer details surrounding line items is pretty straightforward with modern invoice scanners leveraging AI & OCR. Especially for table extraction, there’s been a lot of development, as you can find many online & open-source solutions.
Along with these advancements, modern invoice scanners also come with in-built “data validation” interfaces. This allows AP teams to quickly review and validate the data whenever a potential issue is flagged. Invoice capture software like Nanonets even allow users to specify validation rules that could trigger flags and alert users about potential issues.
Book this 30-min live demo to make this the last time that you'll ever have to manually key in data from invoices or receipts into ERP software.
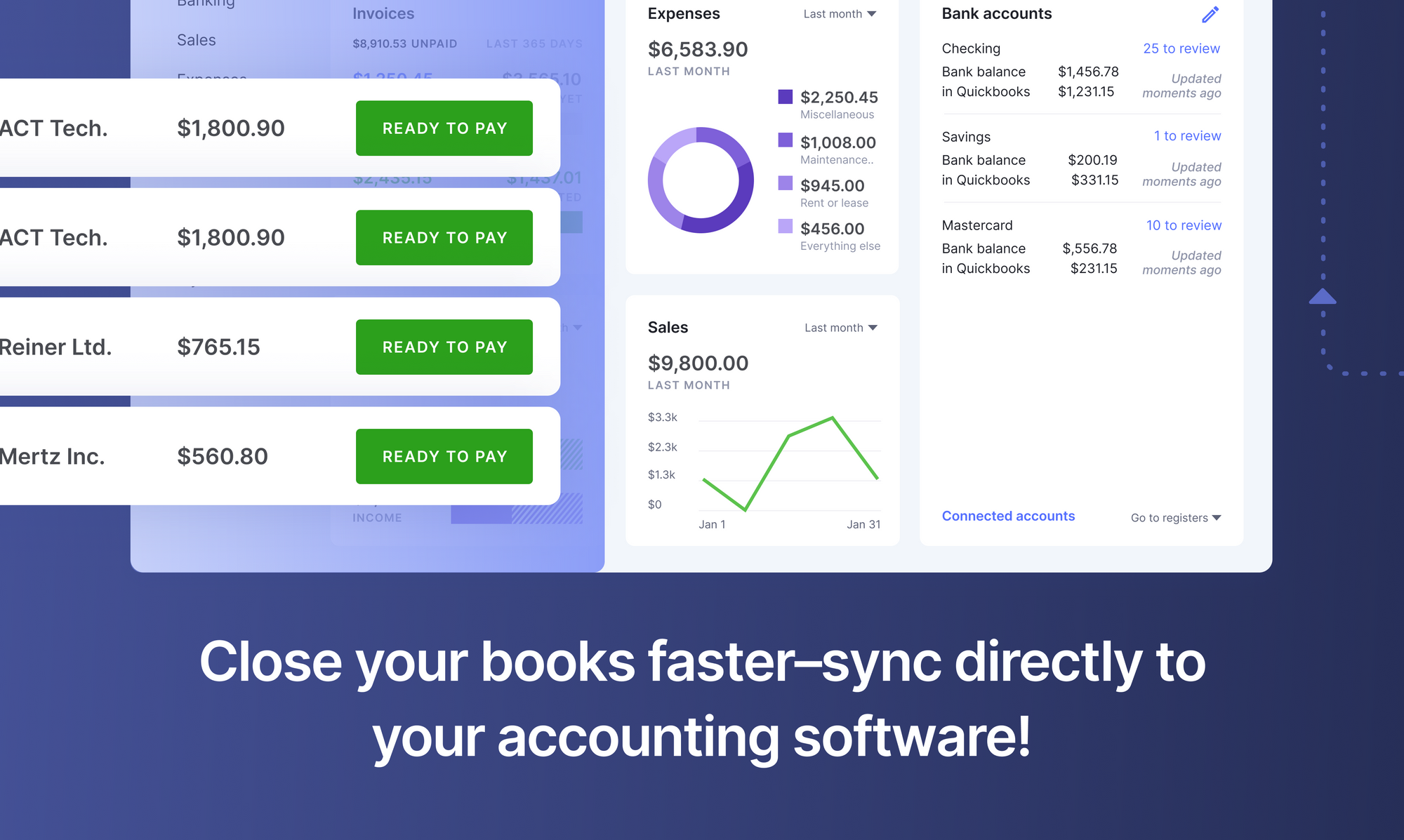
Alternatives to Automated Invoice Capture Software
Most organizations that haven’t adopted invoice automation use one of the methods below to process their invoices. But they each have serious limitations. Here’s an in-depth analysis of these data extraction methods.
Manual copy-paste or data entry - This approach can be slow, erratic & error-prone. A lot of time would be spent in post-processing & verification.
Outsourcing manual data entry - While this approach can reduce data extraction costs, quality control & data security are serious concerns!
Online converters - Online converters have low accuracy levels and can only handle one or few documents at a time.
Table extraction tools - Might require substantial development effort to integrate into in-house workflows. Only works on native PDF documents, so might be tripped up by scanned invoices.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) - EDI “is the electronic interchange of business information using a standardized format; a process which allows one company to send information to another company electronically rather than with paper” (Source). Introduced in the early 70s, this family of technical standards has yet to gain popular acceptance. Unless every related party (or trading partner) adopts EDI, this system would fail.
How Businesses use Invoice Scanning
Invoice scanning use cases for businesses typically fall under 2 broad categories: “known invoice formats” vs “unknown invoice formats”.
Known Invoice Formats
Businesses that deal with a fixed limited set of suppliers and vendors fall under the “known invoice format” category. Such businesses frequently process invoices from the same bunch of suppliers/vendors month after month.
This is common for well-established legacy businesses, brick-and-mortar establishments, wholesalers, and other large businesses. Using automated invoice scanning is ideal in this highly predictable scenario.
- Businesses can use a pre-trained invoice scanner offered by automated OCR software like Nanonets.
- Or businesses can refine the pre-trained invoice scanner to recognize and capture data from the specific types of invoice formats that they receive.
In either case, since the various layouts are known in advance, it is pretty straightforward for automated invoice scanners, like Nanonets, to pick out data fields & line items from these invoices.
Unknown Invoice Formats
Online businesses & e-commerce companies often have to deal with a rapidly changing list of suppliers. Such organizations deal with thousands of invoice formats and could potentially get invoices in new/unknown formats from new suppliers.
Using a pre-trained invoice scanner in this scenario might not provide great results. And refining the invoice scanner through a template-based approach would be very impractical! This is where modern invoice capture software like Nanonets can help.
- Once they are trained on a representative set of invoice formats, they can leverage AI & ML capabilities to take on unknown invoice formats.
- And since they learn continuously from the invoices they process, such automated invoice scanners will only get more accurate with time.
When dealing with unknown document formats, Nanonets recommends/provides a validation interface to quickly review & validate the extracted data. Users can also specify validation rules that could trigger flags and alert them about potential errors or inaccurate data extraction.
Here's a case-study on how a construction company leveraged invoice automation with Nanonets.
Conclusion
Invoice scanners can optimize internal processes for businesses that deal with a large number of invoices and transactions.
Automated invoice scanning improves productivity by redirecting AP teams and other workforce from menial tasks on to higher value generating tasks; directly impacting the bottomline. Such spillover benefits make invoice scanning software suitable even for small/medium businesses that do not process large volumes of financial documents.
So while evaluating automated invoice processing solutions, consider the indirect (intangible) benefits that they provide. Compare these with the cost, product features, ERP integration options, and time/effort needed to set up invoice automation for your specific use case.
Or check out Nanonets OCR API in action and start building custom OCR models for free!
Update Oct 2022: this post was originally published in May 2021 and has since been updated.
Here's a slide summarizing the findings in this article. Here's an alternate version of this post.
