Financial document automation is a game-changer for financial services and the banking industry. Let's take a look at how to set up financial document automation workflows in your company.
From multinational banks and big accounting firms to local insurance agencies and small healthcare providers, businesses of all sizes process hundreds and thousands of financial documents daily. The sheer volume of paperwork can be overwhelming, time-consuming, and prone to errors.
Enter financial document automation, a game-changing solution revolutionizing how companies handle their paperwork, regardless of size or industry.
In this article, you’ll learn how to set up efficient document workflow that save time and reduce error, ways to address common challenges, and AI-based finance tools for different use cases across industries.
Financial document automation
– Jeffrey Zhou, CEO & Founder, Fig Loans
Every company, regardless of its primary business focus, deals with finance-related activities. These activities generate many documents containing critical financial data, such as invoices, bills, payslips, forms, KYC documents, bank statements, asset statements, loans, and tax documents.
These documents contain sensitive information, including personally identifiable information (PII) such as client and vendor names, addresses, identification numbers, and beneficiary details.
For large companies with numerous daily operations, manually managing this data becomes increasingly challenging, time-consuming, and error-prone.
Financial document automation is the solution to all these challenges
Document automation tools, varying in sophistication, can perform different functions to streamline accounting and financial workflows.
A prime example of this is automating the entire loan underwriting process, where speed and accuracy are critical for competing in the modern lending market.
Read About: How to Extract Data from Payslips?
How does financial document automation work?
To understand financial document automation, let's look at a typical Accounts Payable (AP) process:
- AP team issues a purchase order (PO)
- The vendor delivers and sends an invoice
- AP matches the invoice with the PO and delivery receipt
- If matched, payment is processed
This manual process is manageable for small companies. However, as companies grow, the volume of documents increases exponentially, making manual processing inefficient and error-prone.
Financial document automation uses technologies like advanced Optical Character Recognition (OCR), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Machine Learning (ML) to streamline these processes.
Manual vs Automation
Let's compare manual vs. automated AP processes:
| Step | Manual Process | Automated AP Process |
|---|---|---|
| Invoice receipt | PDF in Email | Any format (PDF, image) from any source (Slack, Cloud) |
| Data entry | Manual input into accounting system | AI-powered automatic extraction |
| PO matching | Manual retrieval and comparison | Automatic [2-way, 3-way & 4-way matching] |
| Error checking | Manual review | AI-powered validation with flagging for human review |
| Approval routing | Emails with multiple follow-ups | Automatic routing based on predefined rules |
| Payment scheduling | Manual entry into payment system | Automatic scheduling based on terms |
| Document storage | Physical filing or basic digital storage | Intelligent digital storage with audit trail |
Now, let’s understand the results and RoI in both manual and automated document extraction for the above AP process:
| Metric | Manual process | Automated extraction with AI |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Time | 1-3 days per invoice | 5-10 minutes per invoice |
| Error rate | ~4% due to manual data entry | <1% with AI validation |
| Cost per invoice | ~ $10-$15 | ~$2-$3 |
| Scalability | Limited by human resources | Highly scalable (thousands of documents) |
| Vendor management | Reactive, based on issues | Proactive, based on data insights |
| Employee focus | Data entry and document handling | Strategic financial analysis and vendor relationships |
| Cash flow visibility | Delayed, based on manual reports | Real-time, with predictive analytics |
How to automate financial document workflows
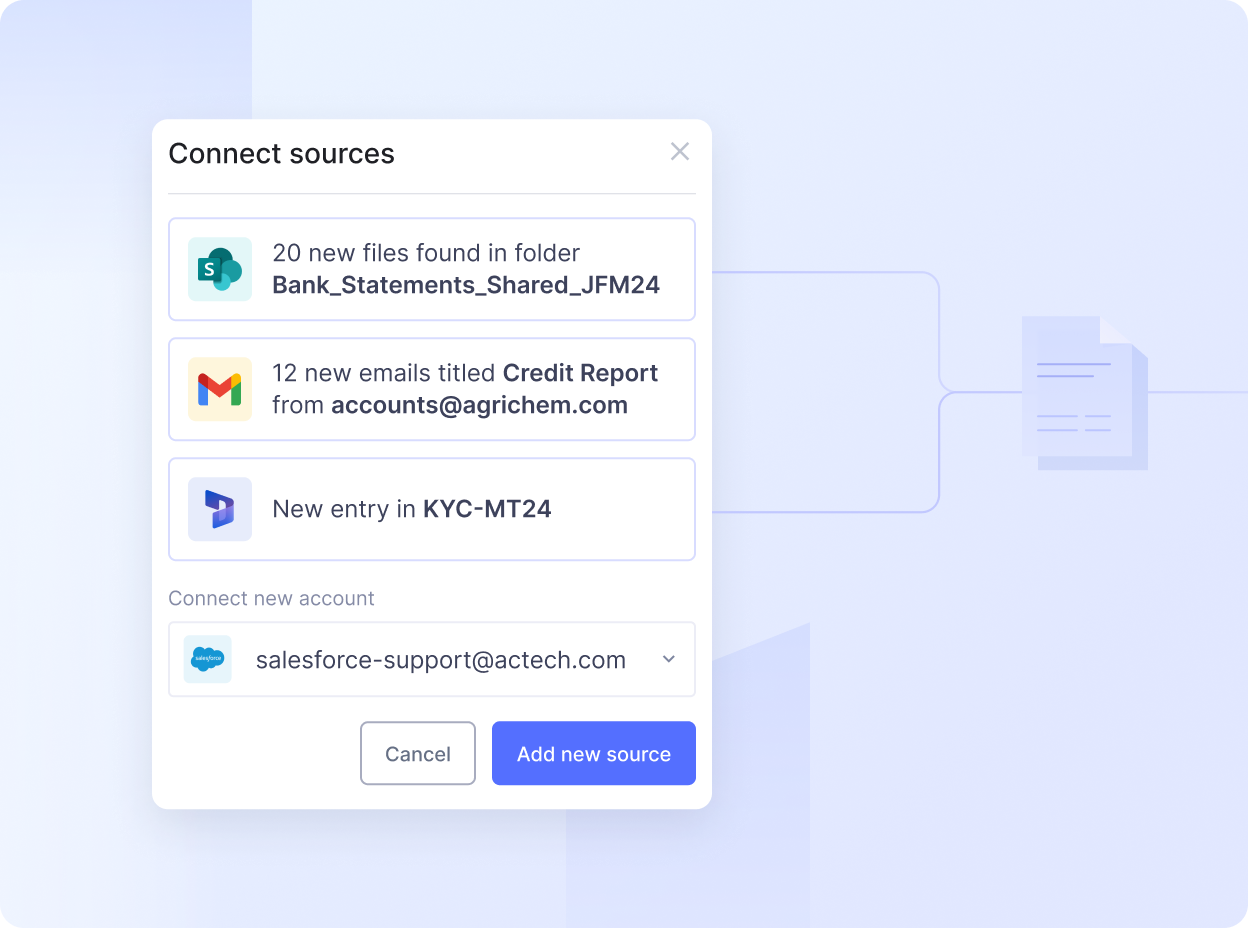
Here’s how you can set up and automate any financial document workflow using Nanonets:
Step 1: Create an account on Nanonets
Step 2: For popular financial documents such as invoices, receipts, POs, bank statements, choose a pre-built extractor workflow.
If you want to set up a new workflow from scratch, choose Create your own workflow and upload a new document.
While you document is getting processed, you can quickly configure your import and export settings depending on the source of your documents.
Step 3: Once the workflow is set up and the document is processed, review the extracted fields in the document and approve it once ready.
Step 4: You can also customize the workflow with different actions such as:
- Adding different formatting steps such as currency detection, change date formats, scan barcode and QR code, parse URL, LLM data actions, etc
- Look up new fields from external sources such as Accounting software, database, ERP tools and
- Setting up rule-based approvals by adding multiple reviewers, conditions for flags and validation rules
- Set up notifications to ensure your team receives timely reminders via Slack and Email
- Customize import and export from 30+ sources
This allows you to set up customized finance document automation workflow for banking, financial services, or any finance processes.
Overcoming concerns and challenges in document automation
While document automation comes with compelling benefits, companies often face several challenges and concerns when implementing these systems. Let's address these issues and explore some practical solutions:
Accuracy and reliability of financial data
Concern: Financial data requires 100% accuracy. Even small errors can lead to significant financial discrepancies or compliance issues. While automation can handle standard document, we encounter exceptional cases regularly that are time-consuming to handle and also raise issues.
Solutions:
- Implement multi-layer verification processes
- Design automation workflows with rule-based paths for exceptions
- Use advanced deep learning models that are trained on industry-specific data
- Incorporate human-in-the-loop systems for complex or high-value transactions
Handling complex and varied document formats
Concern: Financial documents come in multiple formats, languages, and structures, making consistent data extraction challenging.
Solutions:
- Utilize advanced OCR and NLP technologies that work on complex documents (scanned images, PDFs with tables, handwritten documents)
- Train models on a diverse set of document samples
- Implement adaptive learning algorithms that improve over time
- For template-based automated solution, provide options for manual template creation
Security and compliance
Concern: Financial data is highly sensitive, raising concerns about data breaches and maintaining compliance with regulations.
Solutions:
- Choose a reputed automation tool that adheres to national and global compliance and regulatory standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOC2, ISO 27001, FedRAMP (in the U.S.)
- Implement end-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) for sensitive data
- Regularly conduct security audits and penetration testing
- Restrict unauthorized viewing of confidential documents
- Implement strict guidelines to protect client privacy
- Consider on-premise deployment for highly sensitive data.
Integration with existing systems
Concern: We have legacy systems (like SAP) and a complex tech stack, which makes integration challenging.
Solutions:
- Choose an automation solution with robust API capabilities
- Look for pre-built integrations with popular financial software
- Engage IT teams early in the implementation process
- Implement the change gradually, starting with less critical processes
- Train your staff with efficient onboarding
Use cases of financial document automation
Document automation in the realm of finance and accounting is used in many sectors. Let's explore potential use cases and benefits in different industries:
Banking and financial services
This sector deals extensively with financial matters and handles an enormous volume of finance-related documents pertaining to customers, organizations, and internal processes.
Financial document automation is crucial to ease employee stress, improve customer service, reduce turnaround times, and enhance regulatory compliance.
Insurance industry
The insurance sector is another field dedicated to financial matters. Automation tools for handling insurance-related documents can help with rapid information extraction and validation, increased underwriting capacity, accurate risk assessment, faster and automated insurance claims processing, resulting in quicker payouts for policyholders and more efficient operations.
Accounting and auditing firms
Accounting firms and departments in large businesses routinely handle documents with critical financial data. They are responsible for vendor payments, maintaining transaction records, auditing, taxation, and regulatory compliance.
Automating document processing allows these firms to quickly extract financial data from various sources, perform audits with fewer manual steps, and generate reports automatically.
Real estate and property management
Document automation can help real estate companies process large volumes of property data. This makes AI-powered lease abstraction and property valuation more efficient with faster lease processing, improved accuracy in key data point extraction, and better portfolio management. It also allows for quicker property appraisals and improved management of customers, properties, and financial records.
Healthcare
Healthcare is a sector that deals with a large variety of sensitive documents, both financial and non-financial. Apart from patient data, there's payroll management for medical and non-medical staff, infrastructure-related documents, and other financial transactions. Document automation helps healthcare institutions store accurate patient records, process claims more quickly and accurately, and enable faster patient onboarding and transitions.
Manufacturing and supply chain
In the manufacturing and supply chain sector, document automation can significantly improve accuracy in inventory management, reduce processing times for purchase orders and invoices streamline operations, streamline quality control processes and enhance traceability in the supply chain.
