Here in August 2025, the biggest threat to your company's growth isn't a new competitor — it's a decade-old process. AI can now learning to generate entire software workflows from a single sentence and understand business processes by watching a video. Your back office cannot still be running on the same foundation as they were in 2015: email, spreadsheets, and manual data entry.
This growing gap between what's technologically possible and what's operationally practiced is where competitive advantages are won and lost. The question is no longer if you should automate your document workflows, but how quickly you can do so to avoid being outpaced.
This guide is for businesses that want to close that gap. It provides a practical framework to not only modernize your current operations with today's best-in-class AI but also to future-proof them for the next wave of automation. We'll show you how to build a workflow that is not just efficient, but intelligent and ready for what's next.
Why manual document workflows hold you back
Before diving into a solution, we always advise our customers to quantify the problem fully. The true cost of manual workflows goes far beyond the hours spent on data entry. It’s a strategic liability that impacts your finances, your team's morale, and your ability to compete.
The full cost of inaction includes:
- High operational costs: Manual processing requires significant human effort. For instance, growing your business 5x would require a 5x increase in back-office staff to handle invoices, or the AP team would be forced to spend up to 20 hours of a 40-hour work week on manual data entry alone.
- Costly errors and delays: Manual data entry is prone to mistakes, which can lead to incorrect payments, compliance issues, and delayed reporting. These errors then require even more time to fix, creating a vicious cycle of inefficiency.
- Inability to scale: You cannot scale a business on manual processes. As document volume increases, your costs rise linearly, and bottlenecks become more severe, throttling growth. This was the core issue facing a client of ours, Pro Partners Wealth, which found that its manual invoicing process hindered its ability to take on new clients.
- Lack of visibility: When documents live in email inboxes and on shared drives, it's nearly impossible to know the real-time status of a process. This data lag slows down decision-making across the entire organization.
To make this tangible, let’s look at the complex journey of a document at Asian Paints. They had to manage purchase orders, invoices, and delivery notes from a network of over 22,000 vendors. The process involved manually compiling data into a CSV file for upload into their SAP system, manually cross-checking documents, and routing discrepancies for approval over email. Every step was a potential point of failure, delay, and cost. This is the reality that strategic automation aims to solve.
This is not just a problem for the finance team. We see these inefficiencies across entire organizations:
- Human Resources: Managing employee onboarding documents in the US, including W-9 and I-9 forms, or processing pension contribution reports in Canada.
- Legal: Automating contract analysis and managing the lifecycle of agreements
- Manufacturing and logistics: Processing purchase orders, delivery notes, and complex, multi-page Safety Data Sheets (SDS).
By tracing the journey of a single document in one of these areas, you can pinpoint the exact bottlenecks you need to solve.
Map your document ecosystem before you get started
Before you think about whether to go with LLMs like Gemini or ChatGPT or more purpose-built tools, spend a week documenting every document type that flows through your organization.
Create a spreadsheet with these columns: document type, monthly volume, current processing time, number of fields to extract, and downstream systems that need the data. For a mid-sized company processing invoices, this might look like:
- Invoices: 5,000/month, 15 minutes each, 12 fields (vendor name, invoice number, date, due date, PO number, line items, quantities, unit prices, tax, shipping, total, payment terms), feeds into NetSuite and approval workflow
- Purchase Orders: 3,000/month, 10 minutes each, 8 fields, feeds into procurement system
- Receipts: 8,000/month, 5 minutes each, 5 fields, feeds into expense management
This exercise reveals surprising patterns. You may discover that your staff are spending much of their time on receipts that represent only a minute portion of the transaction value.
The document workflow automation landscape
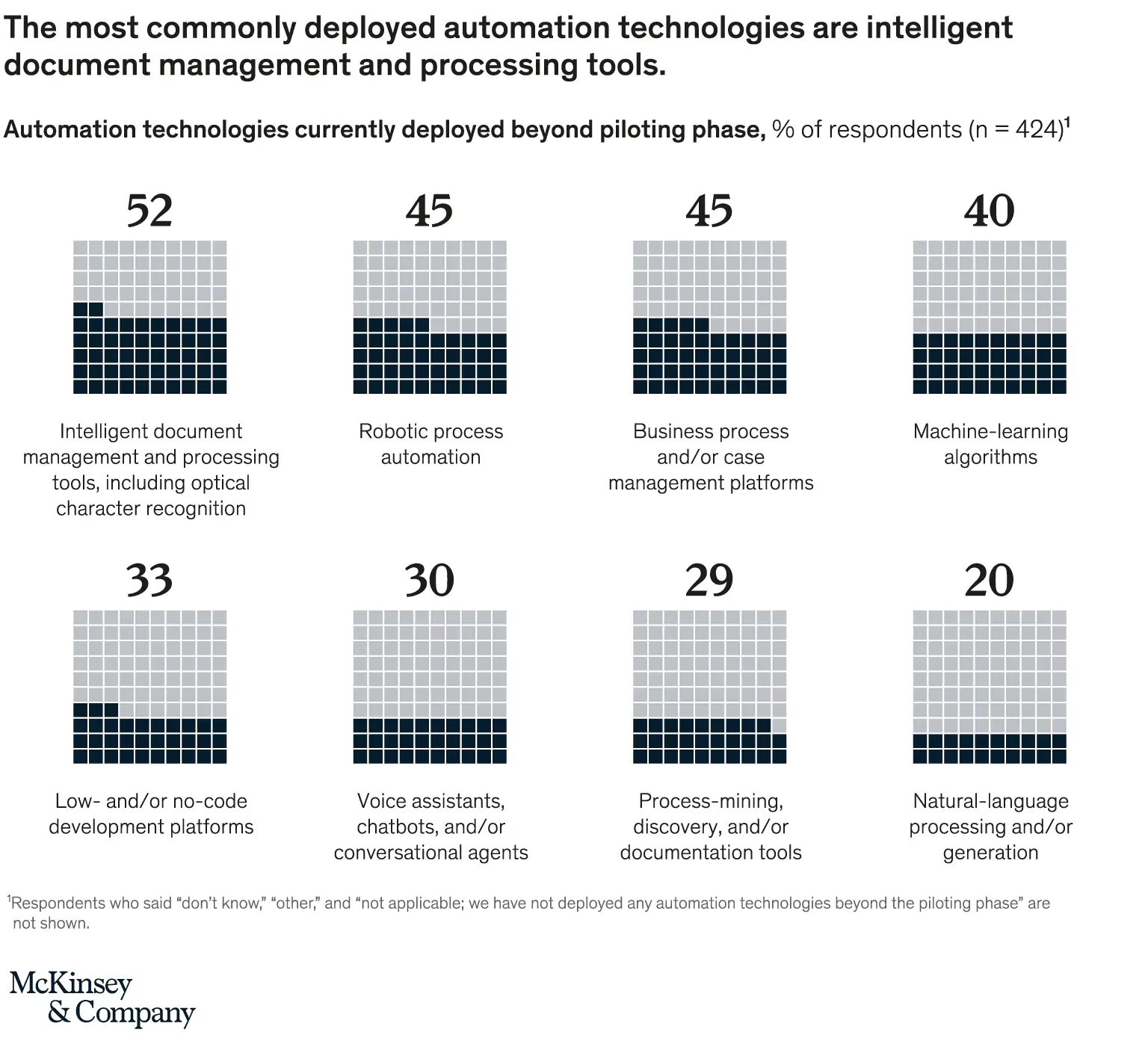
Choosing the right technology is critical, and in 2025, the market is crowded. Understanding the landscape helps you make an informed choice that matches your document complexity and business goals.
a. Legacy tools and template-based OCR
These are the first-generation automation tools, often part of older Enterprise Content Management (ECM) systems. They are rule-based and rely on rigid templates. An administrator defines fixed coordinates on a page and tells the system, "The invoice number is always in this box." The system then applies that fixed template to every document.
- Pros: Can be fast and effective for a single, highly standardized, and unchanging document format.
- Cons: They can be highly ineffective. OCR tools have a high error rate and require manual checks for nearly every invoice because they can't handle variations. For instance, the moment a vendor in Germany sends a Rechnung that looks different from a French Facture, the template breaks, and your automation fails.
b. General-Purpose LLMs (e.g., GPT-4, Claude APIs)
This is a do-it-yourself approach where a developer uses an API from a general-purpose Large Language Model. They write code to send an image or text of a document to the LLM with a detailed prompt asking it to extract information in a specific format, like JSON.
- Pros: Extremely powerful for understanding natural language and unstructured content. They are highly flexible and can be adapted to many tasks with sophisticated prompting.
- Cons: An LLM is a powerful engine, but it's not a complete car. It lacks the essential surrounding enterprise-grade framework: the ingestion pipeline, the data validation rules, the human-in-the-loop review interface, the audit trails, and the direct ERP integrations. You have to build this entire application yourself, which is a significant undertaking. Getting a consistently structured output from a general LLM is a complex challenge in itself.
c. Modern IDP Platforms (Intelligent Document Processing)
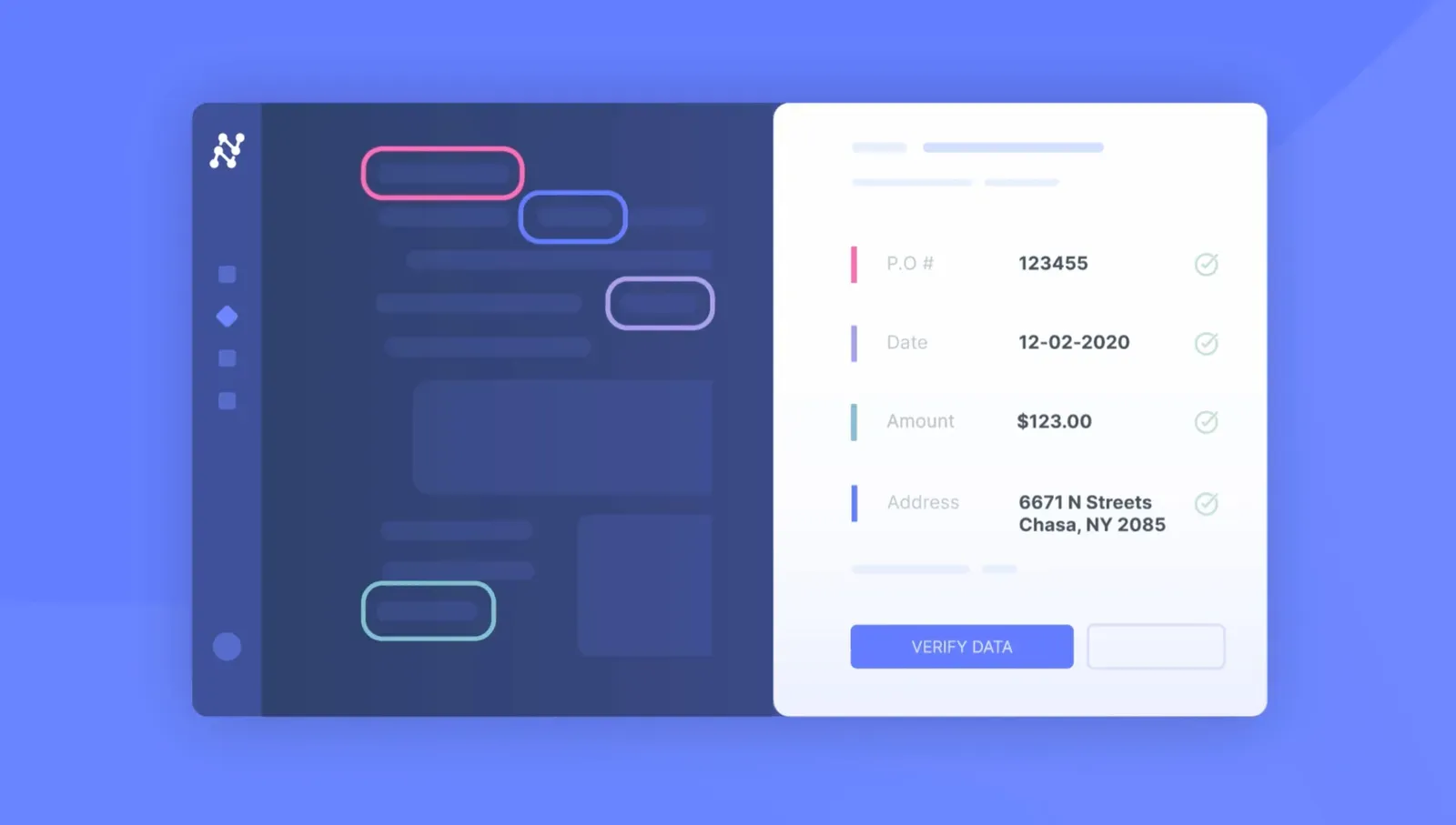
This is the current standard for high-performance automation. These platforms, including Nanonets, combine advanced OCR software with a layer of AI and machine learning. Instead of relying on templates, the AI learns from examples to understand the context of a document, it learns that the text "Invoice No." is usually near the actual invoice number, regardless of its exact coordinates. This allows it to handle a huge variety of layouts for the same document type.
- Pros: They are highly accurate (>95% is a common benchmark), flexible, and template-agnostic. They offer end-to-end workflow automation, from import to export, and continuously learn from user feedback.
- Cons: May require a small amount of initial training data (typically 10-50 documents) to achieve peak accuracy on highly unique or custom document types.
d. Agentic AI
This is the cutting edge of automation. An AI Agent is a system that can perform multi-step reasoning and execute actions across multiple applications to achieve a goal. Instead of just extracting data from one document, an agent could, for example, be tasked to "monitor incoming purchase orders, find the corresponding invoice in the finance system, verify the line items match, and approve for payment if under $10,000."
- Pros: Can handle highly dynamic, complex, and cross-system processes that are impossible for traditional workflow tools.
- Cons: Still an emerging technology that can be less predictable than structured workflow systems.
This is the future we are actively building towards. At Nanonets, our AI Agent feature is a step in this direction, allowing you to give broad, contextual instructions to the AI.
Design your intelligent workflow blueprint
Now that you understand the different types of solutions, let's look at how a modern IDP platform like Nanonets combines the best of this technology into a coherent, end-to-end blueprint. These tools are designed to be both powerful and practical.
Step 1: Establish a central intake
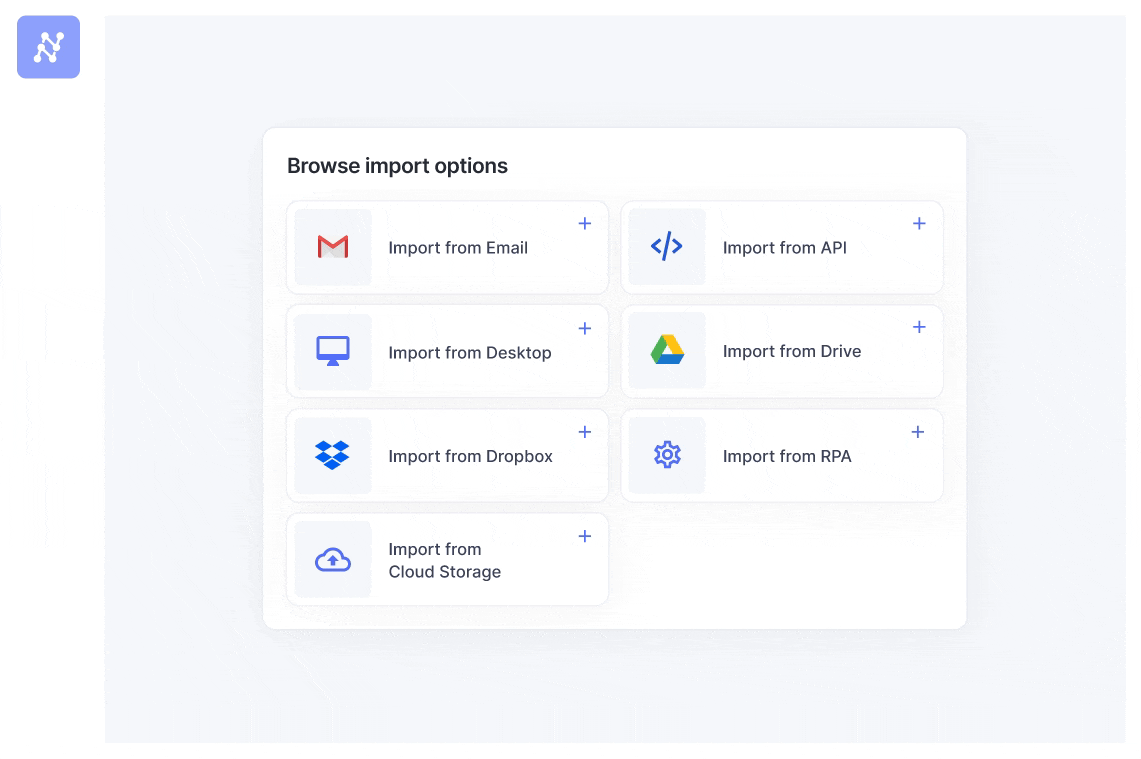
First, centralize how all documents enter your system. Instead of files scattered across inboxes, you create a single, automated point of entry. This can be done by:
- Setting up an auto-forwarding rule from a dedicated email address like invoices@yourcompany.com directly to a unique Nanonets workflow email address.
- Connecting to cloud storage folders like Google Drive, OneDrive, Dropbox, or SharePoint.
- Integrating directly with other software via API.
Step 2: Automate data processing and enhancement
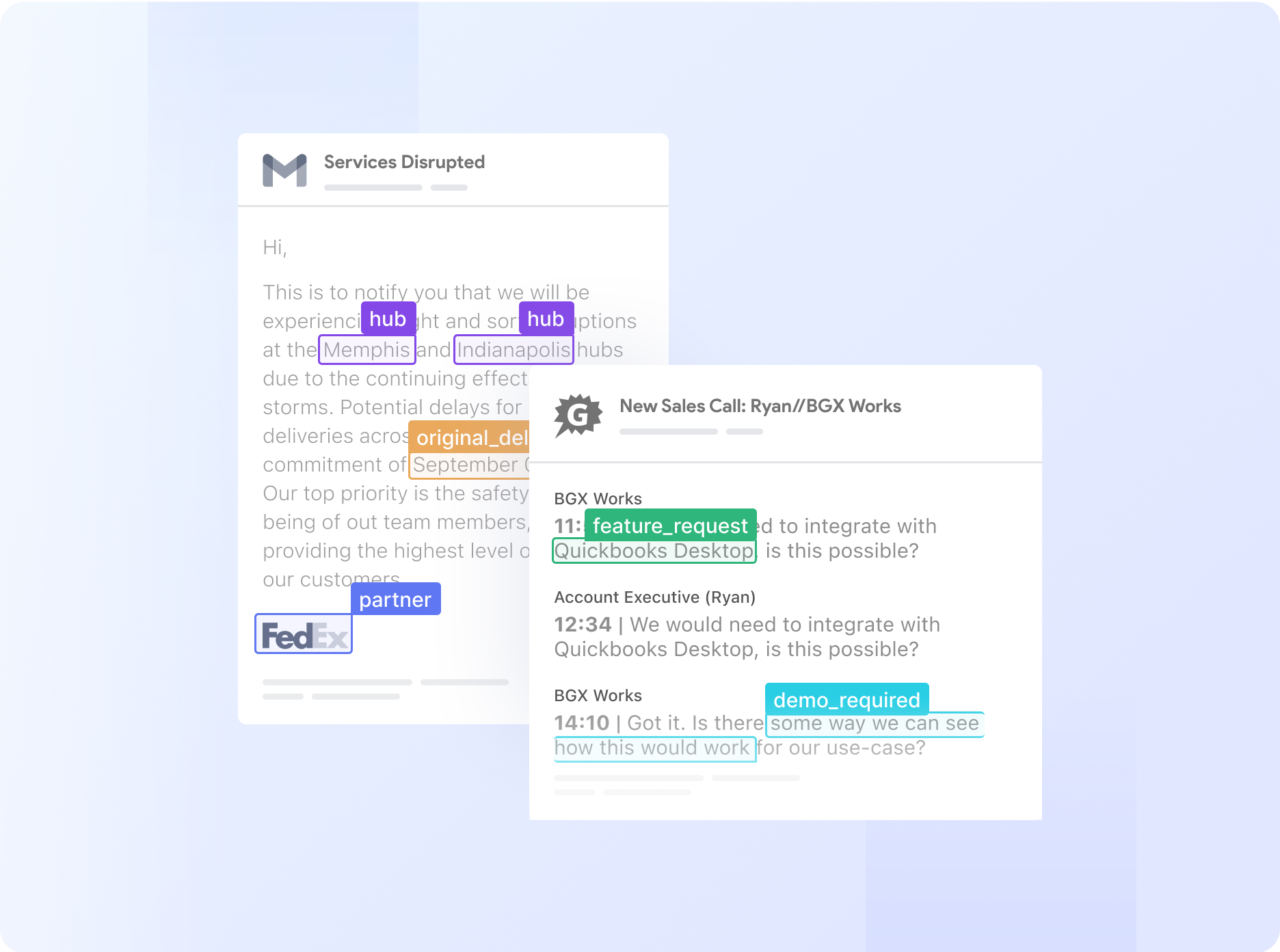
This is the engine room of your workflow, where raw information is transformed into structured, useful data.
- Intelligent data extraction: For a deeper dive into the technology, you can read our guide on AI document processing.
- Data enhancement with "Data Actions": Simple data extraction is rarely enough. The real power comes from automatically cleaning and enriching the data. With Nanonets Data Actions, you can:
- Format Data: Automatically convert dates from the US MM/DD/YYYY format and the EU DD/MM/YYYY format into a standard YYYY-MM-DD format for your database.
- Perform Database Lookups: We helped ACM Services solve a major problem by setting up a lookup that automatically matched the vendor name on an incoming invoice with a master CSV file to pull the correct GL code required by their accounting software.
- Apply Conditional Logic: You can build powerful IF-THEN rules. For example, "IF the seller_name extracted from the document contains 'Fun Express', THEN set the vendor_id field to 'FE-12345'.".
Step 3: Implement business rules and human-in-the-loop
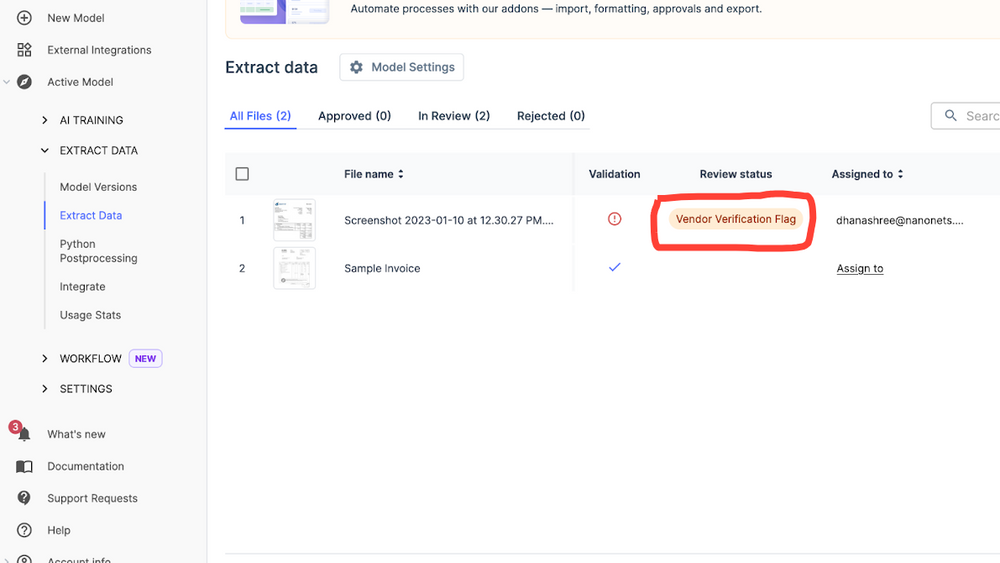
Not every document can or should be processed without a human touchpoint. The approvals stage is where you build in your specific business logic.
- You can set up rules to automatically flag duplicate files to prevent double payments.
- You can create Review Stages that route documents based on their content. A common rule we help clients set up is to flag any invoice where the invoice_amount is greater than $5,000 and assign it directly to a finance manager for manual sign-off before it proceeds.
Step 4: Deliver data to your systems of record
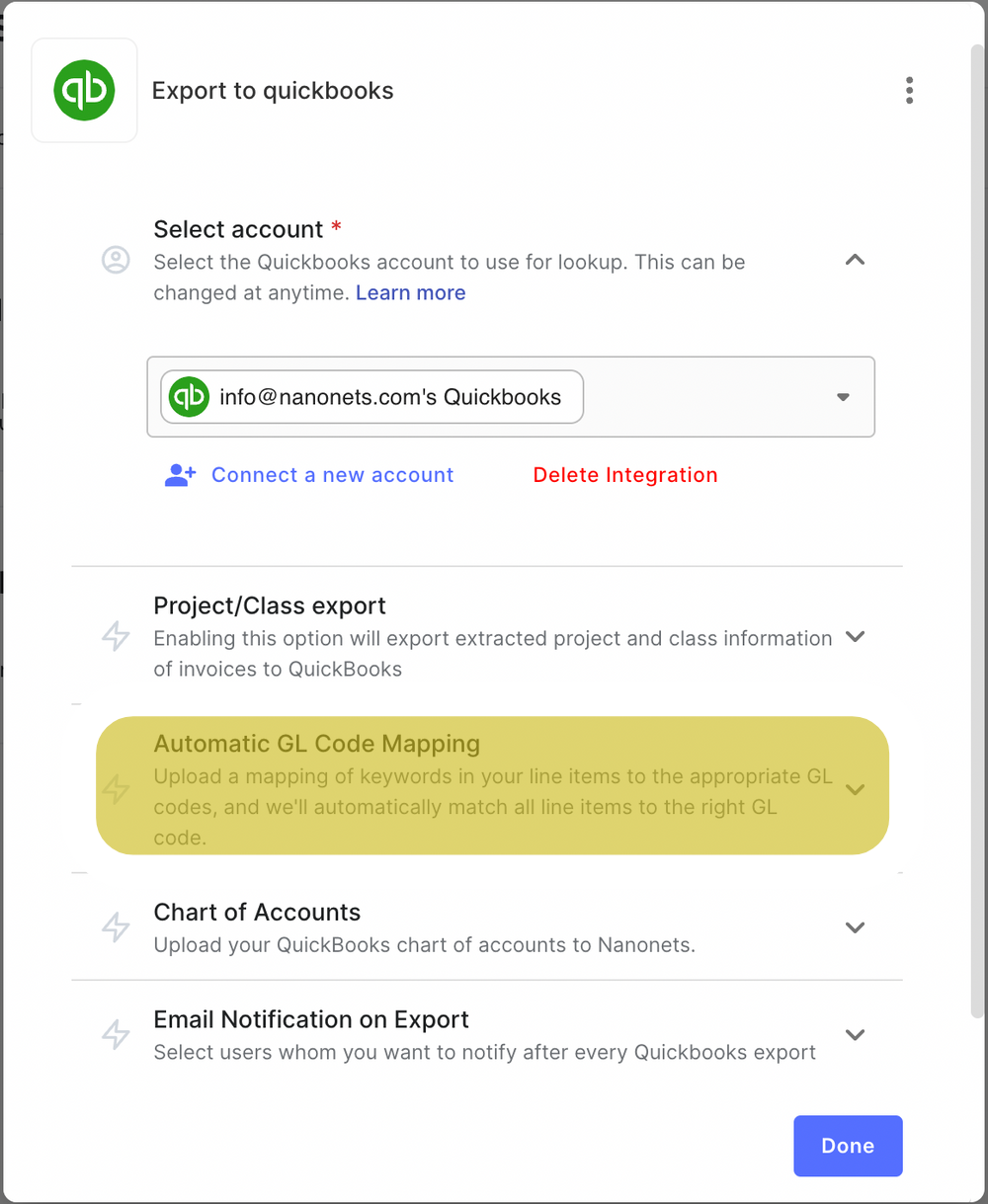
The final step is to push the structured, validated data where it needs to go, closing the loop. We've helped our clients integrate with a vast range of systems, including:
- Accounting software: QuickBooks, NetSuite, Xero.
- ERPs and CRMs: SAP, Salesforce.
- Databases and custom integrations: MySQL, or a flexible webhook for any other system.
A key strategic choice for IT and procurement is the deployment model.
- Cloud-Based (SaaS): This model offers flexibility, scalability, and accessibility. Teams can access, edit, and approve documents in real-time from anywhere. This is the most common and fastest way to get started.
- On-Premise: For organizations with very strict data residency or security requirements, an on-premise solution offers complete control over both hardware and software. At Nanonets, we provide this option via a Docker deployment for our enterprise clients.
Follow proven best practices for high-accuracy AI
Here are the keys:
- Start with diverse data: When training a custom model, we always advise clients to use samples from as many different vendors and layouts as possible. A minimum of 10-50 diverse documents is a great starting point. This is what teaches the AI to be truly template-agnostic.
- Annotate consistently: Ensure your team follows the same rules when labeling data. For example, if you decide to capture the full address under one label, do it that way for every document you annotate. Consistency is key to accurate learning.
- Embrace continuous improvement: The best systems get smarter over time. With our Instant Learning Models, every correction your team makes is used to retrain the AI in real-time. The system's accuracy increases with every single document you approve.
ROI from intelligent automation
This blueprint isn't theoretical. It delivers transformative and highly measurable results. We believe in being data-informed, so here is the hard data from businesses that have put this plan into action.
a. Drastically reduce processing time
StarTex Software (Texas, USA) needed to digitize complex, multi-page Safety Data Sheets. Their manual process took 10 minutes per document. With an automated workflow, they now process them in 10 seconds, a 98% reduction in time.
JTI Ukraine (Kyiv, Ukraine) was bogged down by a manual process for claiming tax refunds on 185,000 excise stamps annually. The end-to-end process took 24 weeks. After automation, it takes under 1 week, a 96% increase in efficiency.
b. Cut operational costs and scale profitably
Property management firm Ascend Properties (United Kingdom) was growing 5x and faced hiring 5 FTEs to handle their invoice volume. By implementing an automated workflow, they now manage the entire process with one part-time employee, saving 80% in processing costs.
GenesisONE (Illinois, USA), an office solutions provider, saves $52,000 annually by automating the work that previously required one full-time employee for their Accounts Payable process.
c. Achieve true touchless automation
Hometown Holdings (Virginia, USA) achieved an 88% straight-through processing rate for its property invoices, meaning the vast majority of its documents now require zero human intervention. This automation was a key factor in their increasing their Net Operating Income by $40,000.
With a clear understanding of the ROI, the final step is to build a practical implementation plan. This playbook covers the key decisions and best practices for a successful rollout.
Final thoughts
Automating your automated invoice processing and other document workflows is one of the highest-impact projects you can undertake to improve your company's operational efficiency.
The path to saving 4,160 employee hours a year, as Hometown Holdings did, starts with mapping a single workflow and redesigning it with intelligence at its core. By following this strategic blueprint, you can move your organization from the friction of manual processing to the velocity of automated success.
FAQs
How many documents do I need to train a custom model?
You can start training a custom model with a minimum of 10 sample files, but for the best results, we recommend starting with at least 50 diverse documents. The more varied examples the AI sees, the better it becomes at handling new, unseen formats.
What integrations are most critical for AP automation?
The most critical integrations are with your accounting software or ERP. We offer pre-built connectors for QuickBooks, NetSuite, Xero, SAP, Salesforce, and more, allowing for a seamless flow of data from the invoice to your system of record.
Can the system handle tables and line items?
Yes. Nanonets is designed to capture tabular data, including line items from invoices with columns like Description, Quantity, Unit Price, and Line Amount. You can also train custom models to recognize any table structure.
What's the difference between a sequential and a parallel workflow?
A sequential workflow is a linear process where one step must be completed before the next begins (e.g., Draft -> Review -> Approve). A parallel workflow allows multiple tasks to happen at the same time (e.g., Legal and Finance review a contract simultaneously). Modern platforms can support both.
What's the difference between a modern IDP platform and a legacy OCR tool?
A legacy OCR tool is typically rule-based and relies on rigid templates, meaning it expects data to be in the exact same place on every document. This approach is brittle and fails when document layouts change. A modern Document Processing platform, like Nanonets, uses AI to understand the context of a document, allowing it to find information regardless of its location. This makes it flexible and able to handle a high variety of formats from different vendors without breaking.
Why not just use a general-purpose LLM API for document workflow automation?
While a general-purpose LLM is powerful for understanding text, it's only an engine, not a complete vehicle for enterprise automation. An IDP platform provides the essential framework around that engine, including:
- Pre-built integrations for ingestion and export to systems like SAP, QuickBooks, and Salesforce.
- A human-in-the-loop interface for validating data and managing exceptions.
- No-code business rule engines for approvals and data enhancement.
- Enterprise-grade security and audit trails. Building this entire framework yourself around an LLM API is a significant and complex development project.
How does the system ensure the security of my documents?
Security is handled through a combination of compliance, encryption, and deployment options. Nanonets, for example, is compliant with standards like SOC 2, GDPR, and HIPAA. Data in transit, such as through email import, is protected with TLS encryption. For organizations with the strictest data security requirements, an on-premise deployment via a Docker container is also an option, ensuring no data ever leaves your own servers.
What are the most common integrations for an automated workflow?
The most critical integrations are with your systems of record. Based on real-world use cases, the most common integrations are with:
- ERPs: SAP, NetSuite
- Accounting Software: QuickBooks, Xero, Sage
- CRMs: Salesforce
- Cloud Storage: Google Drive, OneDrive, SharePoint
- Databases: MySQL, MSSQL, PostgreSQL