
A new invoice arrives in your inbox. And as you begin processing it, you get a sense of déjà vu. The address and the amount – you've seen this before, but not sure where. So you start searching, scrolling through endless spreadsheets and folders, trying to find a match...
Sound familiar? This scenario plays out in countless AP departments worldwide.
Imagine a system that could instantly flag duplicate invoices, extract data with precision, and even learn from its mistakes. AI invoice processing can do that and a whole lot more. PS: That's also what we have built at Nanonets.
1. AI's role in invoice processing
2. The practical applications
3. How to implement it in your organization
What is AI invoice processing?
AI-based invoice processing uses artificial intelligence to automate invoice data capture with AI, extraction, recognition, validation, and processing. Furthermore, it can route the extracted data through the appropriate channels and tools for approval and payment.
This automated workflow reduces manual work, improves accuracy, and speeds up the entire process from receipt to payment.
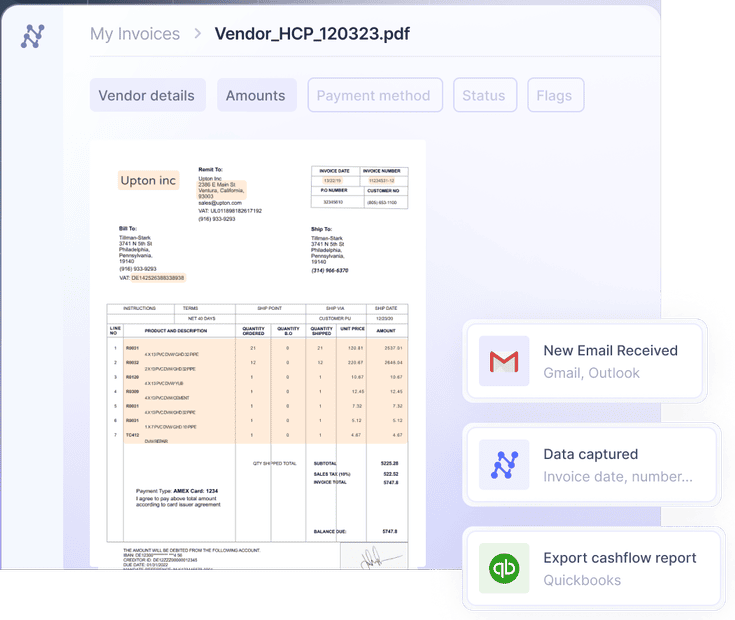
Critical technologies in modern invoice processing:
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR) converts text from invoice images or PDFs — implemented with a layer of AI for enhanced accuracy.
- Machine Learning (ML) analyzes invoice data, identifying patterns and improving accuracy over time.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) interprets text context, regardless of language or format.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive tasks based on predefined rules—often combined with AI to handle more complex tasks.
These core technologies form the foundation for various AI-powered invoice processing solutions. For starters, you have Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT being used to interpret invoice data and extract relevant information.
I've noticed that many accounting tools have started incorporating AI into their workflows. For instance, QuickBooks has something called Intuit Assistant, which can help you identify overdue invoices, draft email reminders, and so on.
Microsoft's Power Platform offers AI builders – essentially, low-code tools for creating custom document processing solutions. You can also use it to process invoices.
And lastly, you've Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) platforms. They combine OCR, ML, NLP, and workflow automation to automate the process end-to-end, from capturing invoices, extracting data, and validating information to integrating with accounting systems and ERPs.
Manual vs. automated invoice processing - Key differences
But these numbers only tell part of the story. What you really want to know is how this happens and what it means for your team. Let me break down the key differences between manual, semi-automated, and fully automated processing:

Manual invoice processing
You get invoices via email, mail, or fax. An employee manually sorts them and checks vendor information, invoice numbers, line items, and other details for completeness. The data is then manually entered into accounting systems.
Next, it is verified through a three-way matching process, comparing the invoice against purchase orders and delivery documentation. It then moves through an approval workflow, where designated individuals review and sign off. Once approved, the payment is scheduled and processed according to vendor terms. Finally, all documents are archived for record-keeping and audit purposes.
There are just way too many manual touchpoints. It makes the process time-consuming, error-prone, and lacking visibility. And if you're using spreadsheets for compiling and tracking invoice data, you're adding another layer of complexity and potential errors.
Semi-automated invoice processing
You might be using this approach right now. It's what happens when companies start digitizing their process but aren't ready for full automation. You set up templates for different invoice formats, use basic OCR to pull out the data, and map it to your accounting system.
Sounds better than fully manual, right? Well, yes and no. While it speeds things up, you still need people to validate the data, handle exceptions, and chase approvals. Plus, every new vendor means creating another template.
Fully automated invoice processing
This method incorporates artificial intelligence and machine learning into invoice processing workflow. For starters, invoices from various sources (email, EDI, forms) are automatically imported for processing. AI works with OCR to extract data accurately, regardless of format.
The system validates extracted data against predefined rules and existing records, flagging exceptions for human review while processing routine invoices automatically. Three-way matching occurs instantly, and invoice approval workflows are digitized with automated notifications. Tools like three way match NetSuite are often used to streamline this process, ensuring accurate validation and compliance. Once approved, payment is triggered based on predefined terms.
AI-powered systems continuously learn from each processed invoice, adapting to new formats and improving accuracy over time.
Here’s a table offering a quick overview of manual, semi-automated, and fully automated invoice processing workflows and how they differ:
| Process Area | Manual Processing | Semi-Automated Processing | Fully Automated Processing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processing Speed | Baseline | 2-3x faster | 5-10x faster |
| Error Rate | 3-5% error rate | 1-2% error rate | <0.5% error rate |
| Cost Savings | Baseline | 30-50% cost reduction | 60-80% cost reduction |
| Staff Productivity | 100% time on processing | 50% time freed for analysis | 80% time for strategic tasks |
| Scalability | Requires new hires to scale | Requires new hires to scale | Can handle 5-10x volume |
| Payment Accuracy | 90-95% on-time payments | 95-98% on-time payments | >99% on-time payments |
| Audit Readiness | Days to prepare | Hours to prepare | Minutes to generate reports |
Practical applications of AI in invoice processing
Now, let's bring things back to the everyday running of your AP department. How does AI invoice processing impact their day-to-day functions? The answer lies in its ability to transform tedious, repetitive, manual intervention-heavy tasks into streamlined processes.
Let’s explore some automated workflows that your AP team can set up to quickly improve their operations:
1. Automate data entry
AP teams often spend hours manually scanning invoice data and inputting it into different systems. It risks errors that can lead to payment issues and financial discrepancies.
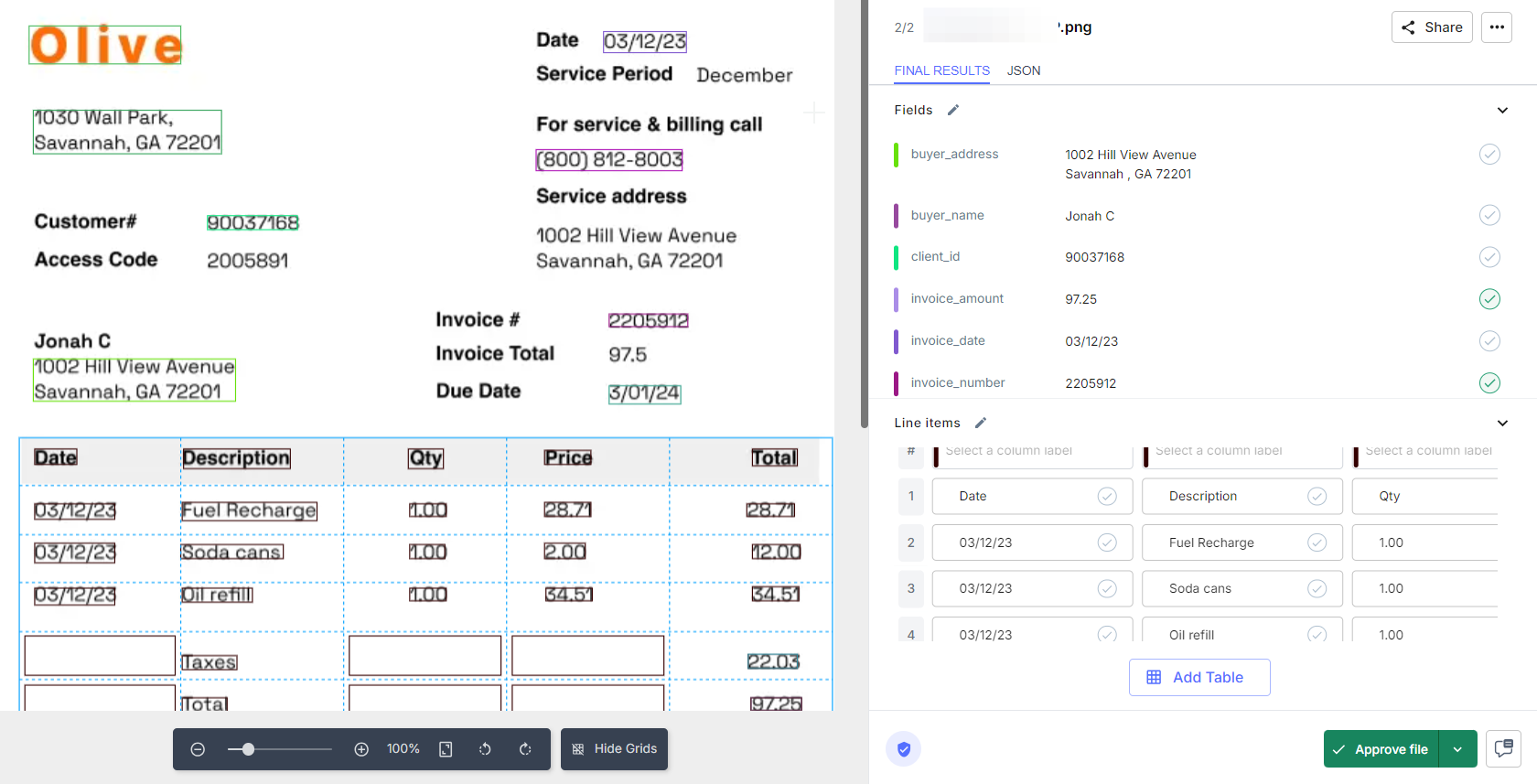
OCR extracts data from structured documents. Add AI, and it gets smarter. AI-powered OCR understands context, adapts to different invoice formats, and learns from corrections.
Your AP team just needs to upload invoices. The system does the rest, from data extraction to populating fields in your accounting software. It also handles PDFs, images, and scanned documents with ease. No more conversions or copy-pasting.
2. Intelligent document sorting
Manually sorting through various documents like invoices, purchase orders, and receipts is time-consuming and prone to misclassification, leading to processing delays and potential compliance issues.
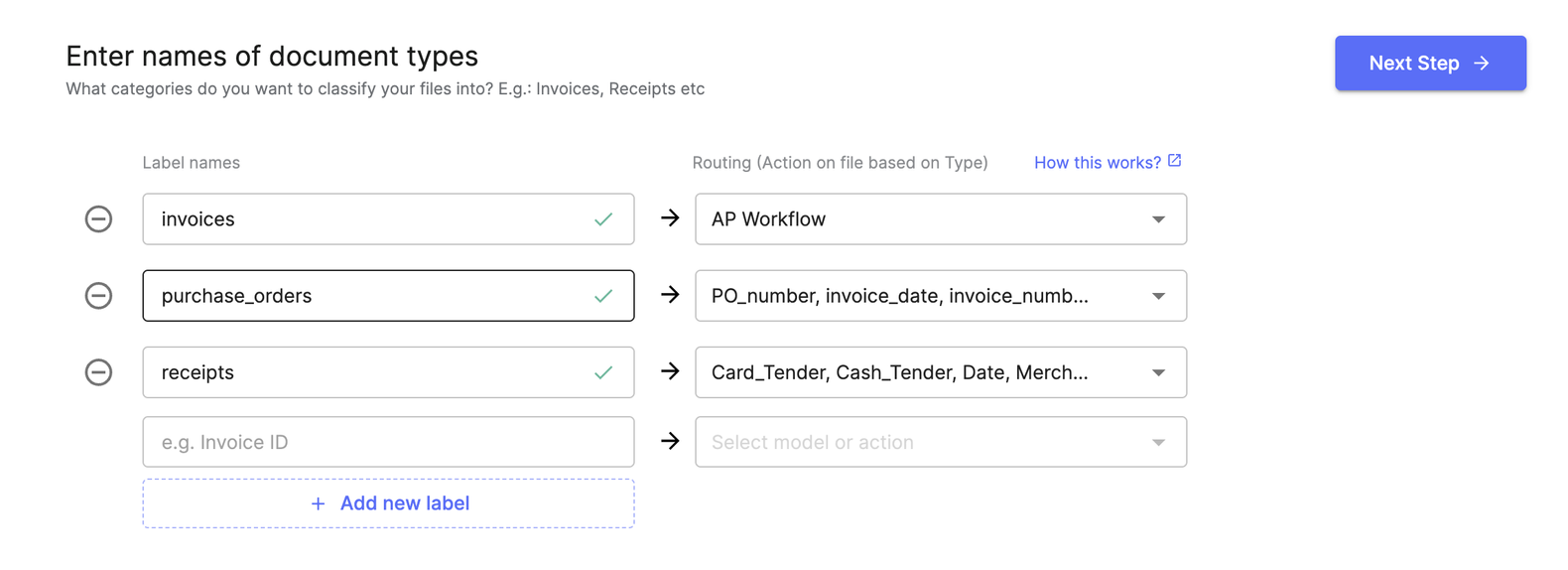
AI-powered tools enable you to create document classification models that route the incoming documents to the correct OCR model. In this case, you can set up AI to automatically classify invoices, purchase orders, or receipts and route each to the appropriate processing workflow. This eliminates manual sorting and reduces the risk of misplaced documents.
3. Smart three-way matching
Manually sorting through various documents like invoices, purchase orders, and receipts is time-consuming and prone to misclassification, leading to processing delays and potential compliance issues.

Some IDPs offer three-way matching capabilities that automatically match invoice data with corresponding purchase orders and receiving documents. The AI compares key fields like item descriptions, quantities, and prices to identify discrepancies. If a mismatch is detected, the system flags it for manual review.
4. Exception handling
Manually reviewing every invoice for errors, discrepancies, or missing information is time-consuming and can lead to processing delays or payment errors.
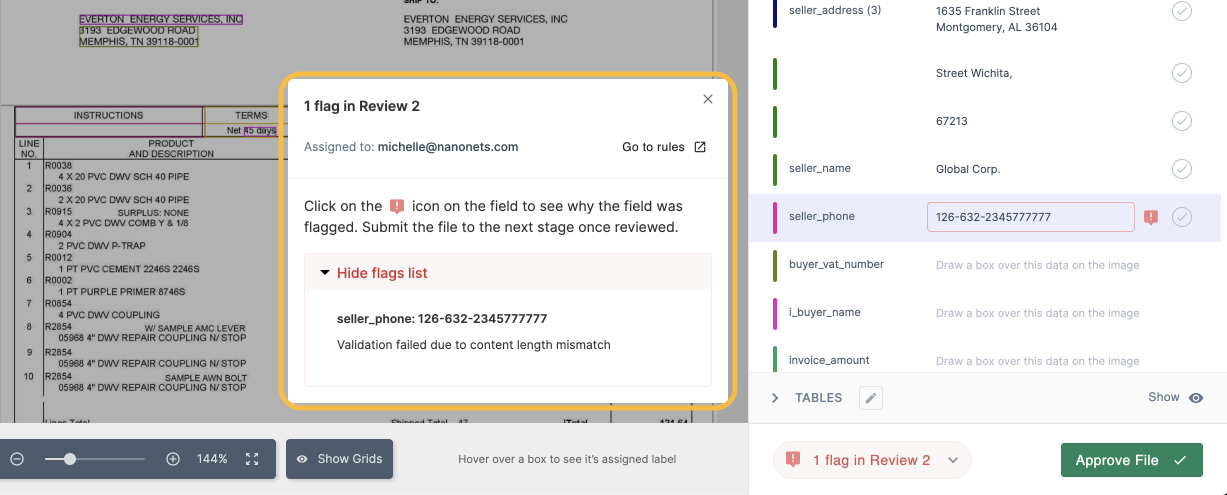
AI-powered invoice processing solutions offer specific rules to automatically flag invoices with missing information, pricing discrepancies, or other anomalies. For example, you can set up AI to flag invoices with amounts exceeding $5,000 for senior manager approval.
5. Invoice coding and GL mapping
Manual invoice coding to correct general ledger accounts is time-consuming and prone to errors, leading to inaccurate financial reporting and compliance issues.
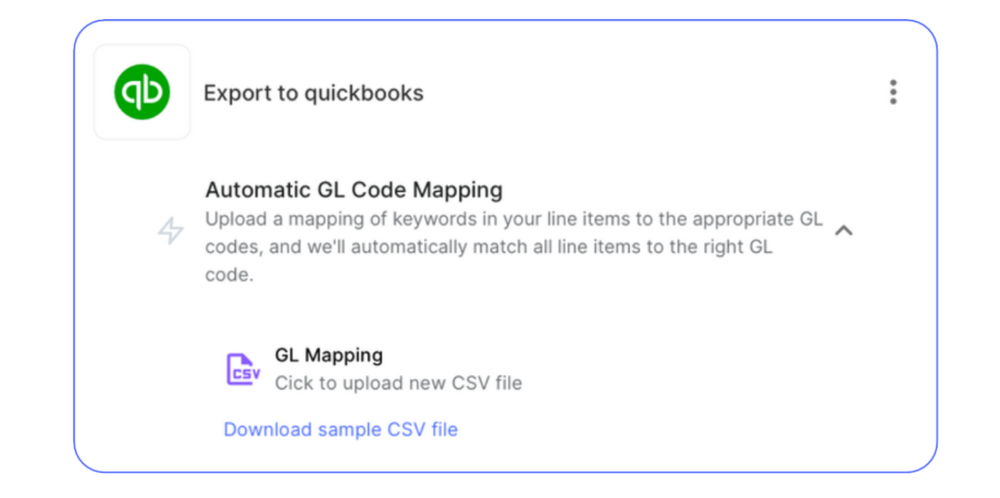
Intelligent automation tools can trained to automatically assign the correct general ledger codes to invoice line items based on historical data, reducing the need for manual coding. The system analyzes patterns in your existing data to predict and apply the appropriate codes, even for complex or multi-line invoices.
6. Duplicate invoice detection
Identifying duplicate invoices is a pain. More so when you have a huge stack of invoices to process. This can lead to double payments, causing financial losses and reconciliation headaches.
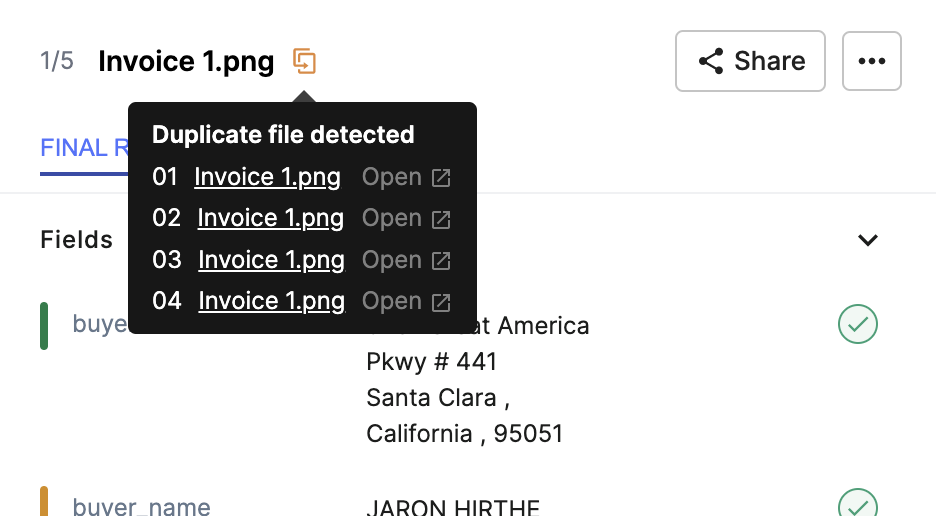
AI-powered systems can automatically identify duplicate invoices. It can compare critical fields like invoice numbers, dates, and amounts across large datasets. When a potential duplicate is detected, the system flags it for review, preventing double payments and reducing financial risks.
7. Line item extraction and categorization
When you are processing complex invoices with multiple line items across multiple pages, things can get tricky. Items may not be in the same order or format on every invoice, making manual extraction and categorization time-consuming and error-prone. This can lead to incorrect expense allocations and inaccurate financial reporting.
With IDP solutions, you can identify, categorize, and download complicated line items on invoices, even when they span multiple pages or have complex structures. This capability accurately extracts detailed information such as item descriptions, quantities, unit prices, and totals.
8. Invoice approval routing
Tired of chasing invoice approval from managers? Manual routing of invoices for approval is often slow and inconsistent, leading to delays in payment processing and potential bottlenecks in the accounts payable workflow. This can strain vendor relationships and result in missed early payment discounts.
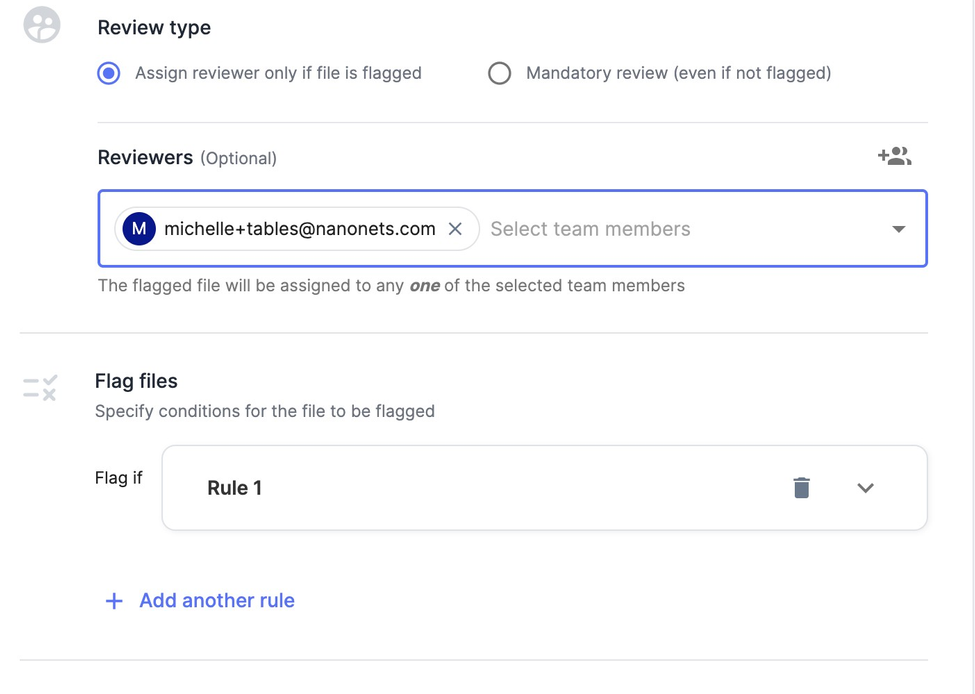
With IDP tools, you can automate the invoice approval process based on predefined rules. For example, you can set up the system to automatically route invoices to the appropriate approvers based on criteria such as invoice amount, department, or project code.
9. Enhance data
Imagine switching tabs and trying to match vendor names against your approved vendor list or verifying invoice numbers against previous records. It often leads to errors, missed discrepancies, and time wasted on data validation.
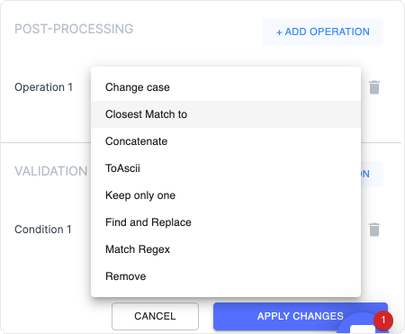
With AI-powered IDP tools, you can automatically match vendor names against your approved vendor list to flag discrepancies. You can also use it to verify invoice numbers against your database to prevent duplicate payments. Moreover, you can automatically populate additional fields (like vendor ID or payment terms) based on matched database records.
You can also use this for non-PO invoice processing. Here, the extracted data can be matched against various databases and systems—the vendor name with your approved vendor database and the invoiced amounts against contracts or purchase requisitions. You can even populate GL codes or cost centers based on historical data.
10. Multi-language support
Processing invoices from international vendors often requires manual translation or specialized staff, leading to delays and potential misinterpretations. This can result in payment errors, compliance issues, and inefficiencies in global operations.
AI-powered OCR can extract and understand invoice data in multiple languages, eliminating the need for manual translation. These systems can automatically detect the language of the invoice and extract relevant information, regardless of the origin or format.
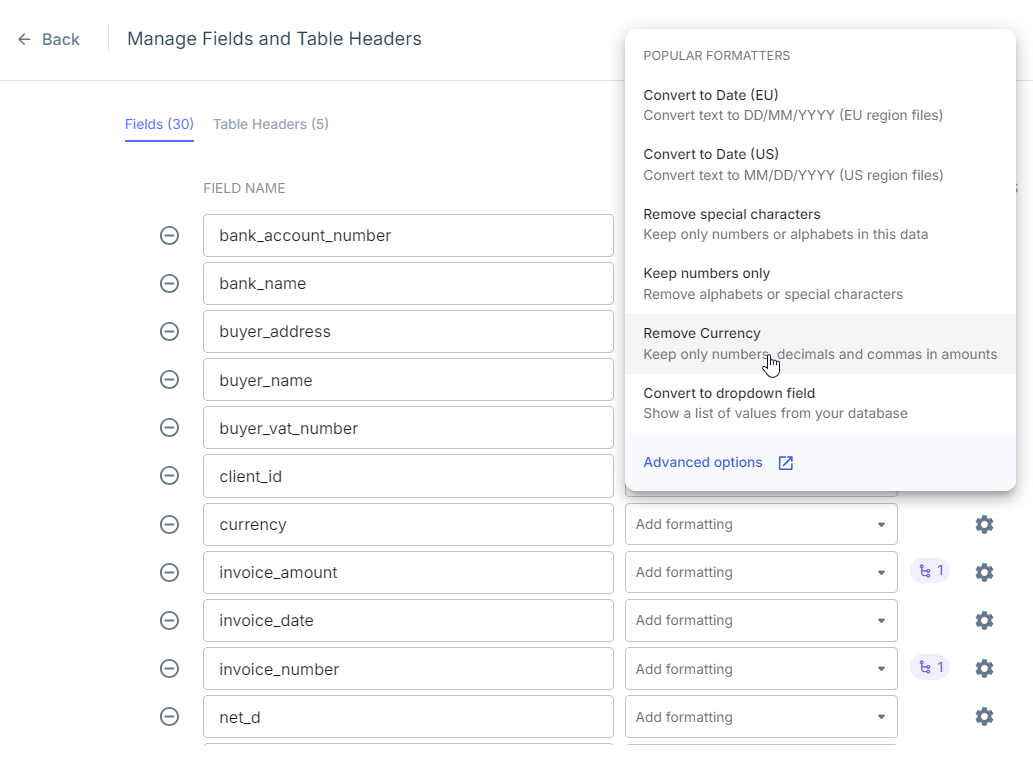
11. Ensure data consistency
Inconsistent data formats across invoices can lead to errors in processing and reporting. Manual standardization is time-consuming and prone to mistakes, especially when dealing with large volumes of invoices from various vendors.
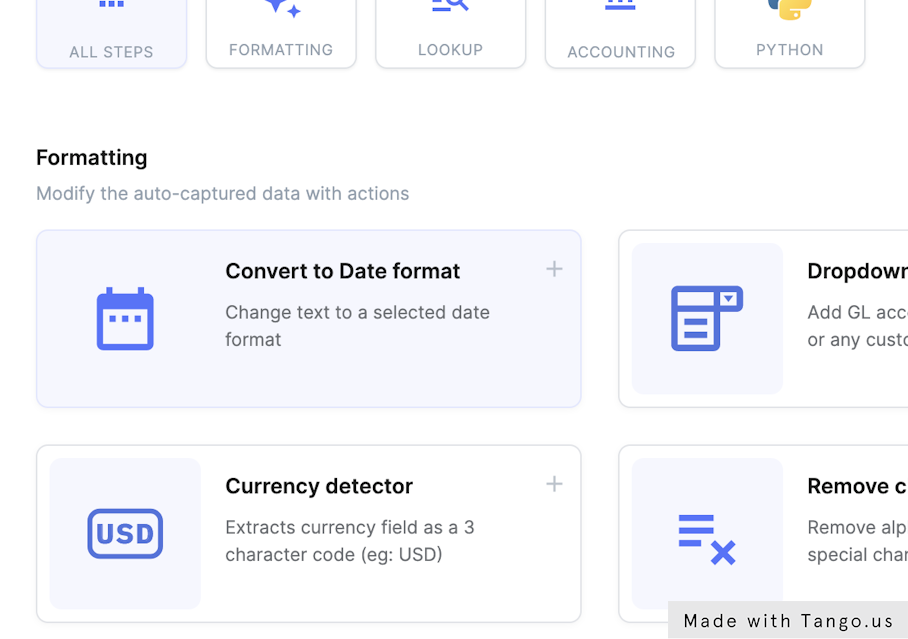
IDP tools allow you to format and normalize extracted data to ensure consistency. It can handle tasks like converting different date formats (e.g., MM/DD/YYYY to YYYY-MM-DD), removing special characters from numeric fields, or standardizing vendor names (e.g., "ABC Corp." and "ABC Corporation" to a single format).
Great product and customer support. - 10/10 would recommend!

"Nanonets is able to reference our significant list of unique product lines and assign them to the correct GL in Quickbooks and other systems. All while maintaining above 90% accuracy without our team having to touch anything. It has saved us countless hours of data entry."
— Kale F., Director of DVM Office, in a review on G2.
How to implement AI in invoice processing in your business
Implementing AI in invoice processing can revolutionize your accounts payable workflow, but choosing the right approach is crucial. AI in accounts payable offers several ways to enhance invoice processing, each with its own strengths and considerations.
Let's explore three popular approaches:
- Large Language Models (LLMs)
- Microsoft's AI Builder
- Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) solutions
We’ll explore the advantages and limitations of each approach to help you make an informed decision.
1. Large Language Models (LLMs)
LLMs like GPT have gained considerable attention over the past few years. These generative AI models excel at identifying and learning from patterns in their massive training data. Based on this, they can generate outputs that resemble the training data.
So, if you upload an invoice to an LLM like GPT, it can analyze the content and perform various natural language tasks, such as text completion, categorizing expenses. summaries of invoice data, and question answering.
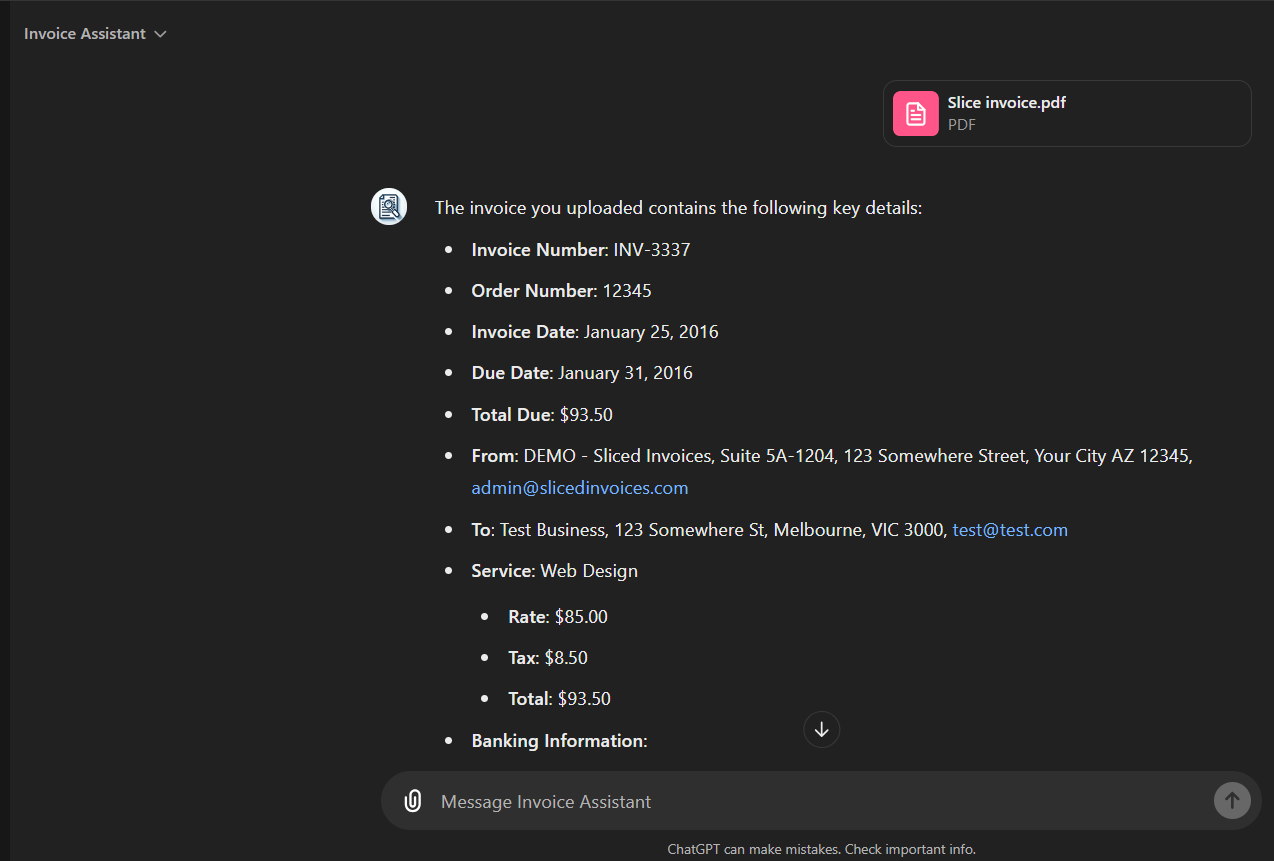
Here's how generative AI work for invoice processing:
- The invoice (in various formats like PDF, image, or text) is fed into the LLM along with a specific prompt.
- The LLM analyzes the invoice content, identifying critical information such as vendor names, invoice numbers, due dates, and line items. It recognizes patterns and similarities to the invoices it has seen during training.
- The LLM then generates a response based on your prompt or instruction. For example, if the prompt asks for a summary of the invoice, the LLM might generate a concise paragraph highlighting key details like the total amount due, payment terms, and vendor information.
- You can copy the generated output for populating fields in your invoice processing system or creating reports for review.
They offer tremendous flexibility, both in terms of usability and integration. Since they are prompt-based, you can easily customize them for your specific invoice processing needs. You can easily build on top of LLMs using APIs and workflow automation tools like Make or Zapier.
But it also comes with significant limitations. For starters, these LLMs may hallucinate or generate inaccurate information. These models are trained on large datasets and try to predict the most likely next word or phrase based on patterns they've learned. They don't have a true understanding of the information they process. So, outputs can vary even for identical prompts, making results unreliable.
LLMs are general-purpose tools that are not optimized for the specific requirements of invoice processing. They may struggle with exact numerical data extraction and complex financial rules. Moreover, processing sensitive financial information through external LLM services raises data security issues.
While LLMs show promise in certain areas, their limitations make them less suitable for the precise, consistent, and secure requirements of invoice processing.
2. Microsoft's AI Builder
Microsoft's AI Builder is a component of the Power Platform that allows users to incorporate AI capabilities into their business processes with minimal coding. It offers a pre-built model for invoice processing that can be customized to an organization's needs.
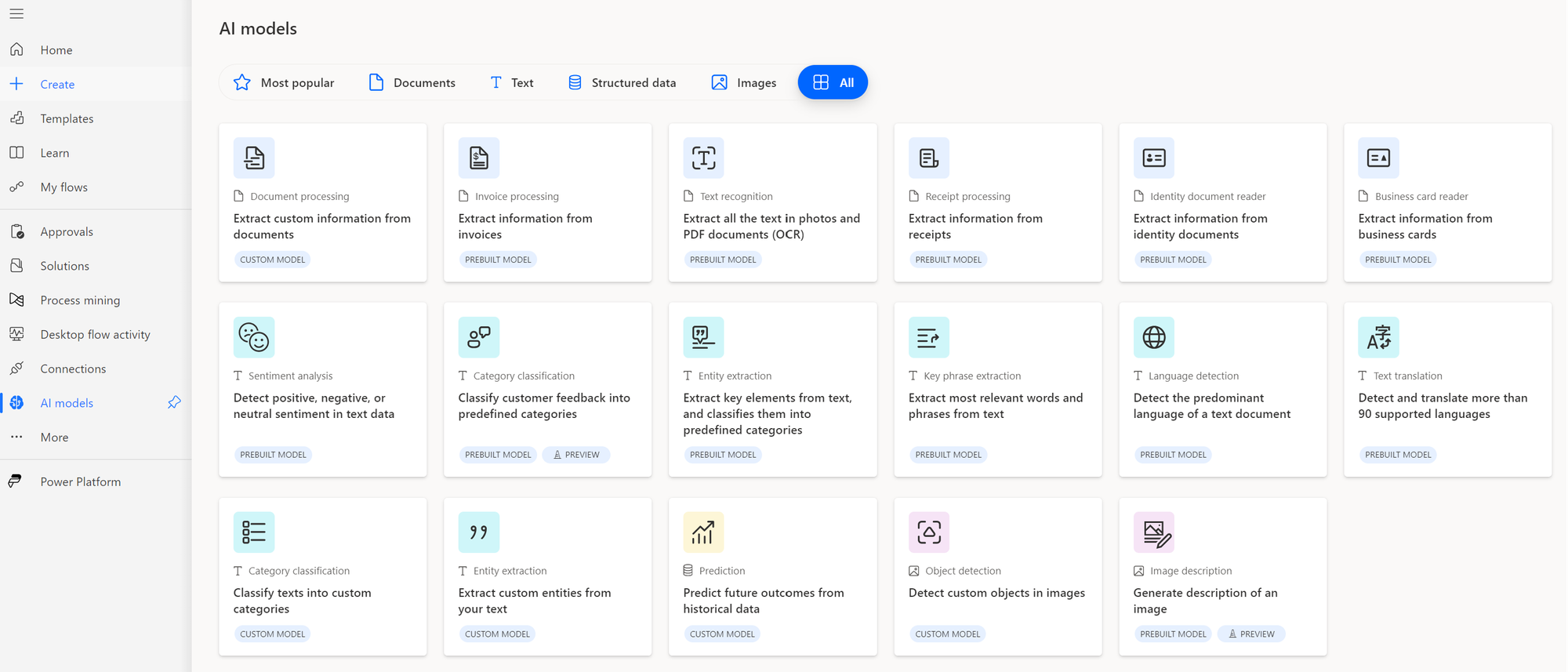
How it works:
- Upload sample invoices to train the AI model or use the pre-built invoice processor.
- The model is integrated into Power Apps or Power Automate workflows.
- When new invoices are received, the AI extracts critical information like invoice numbers, dates, and amounts.
- Extracted data can be used in Microsoft applications or exported to other systems.
AI Builder has some perks. It's user-friendly, especially if you're familiar with Microsoft products. You don't need to be a coding whiz to set it up, and it plays well with other Microsoft tools you might be using.
But it's not without its challenges: It works best with consistent invoice formats. You might struggle to get accurate results if you're dealing with many different layouts. Then, training the model can be tricky. You might need more samples than you'd expect to get good results.
Moreover, it's not great at handling complex or unusual invoice formats. You might hit some performance snags if you're processing a high volume of invoices. Overall, while it's a good starting point, it lacks some advanced features you'd find in specialized invoice processing tools.
In a nutshell, AI Builder can be a good fit if you're already using Microsoft tools and want a simple way to automate some of your invoice processing. But if you're handling a large volume of complex invoices from different sources or need more specialized features, you should look into dedicated Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) platforms. They're designed specifically for tasks like invoice processing and often offer more robust and scalable solutions.
3. Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) solutions
When it comes to invoice processing, businesses need reliable, consistent results. This is where IDP solutions shine. Unlike more general AI tools, IDP platforms are built specifically for tasks like invoice processing, offering a more predictable and accurate approach. They're designed to handle all sorts of invoices - from simple to complex, typed to handwritten - with high accuracy.
What sets AI invoice processing systems apart is their ability to deliver consistent results time after time, regardless of the invoice format or complexity. IDP solutions work methodically, following set rules and patterns while also learning from each document they process. This means they can adapt to new invoice formats over time but in a controlled, predictable way.
Here's how to implement AI invoice processing using Nanonets as an example:
Step 1: Sign up for Nanonets and log in to your account.
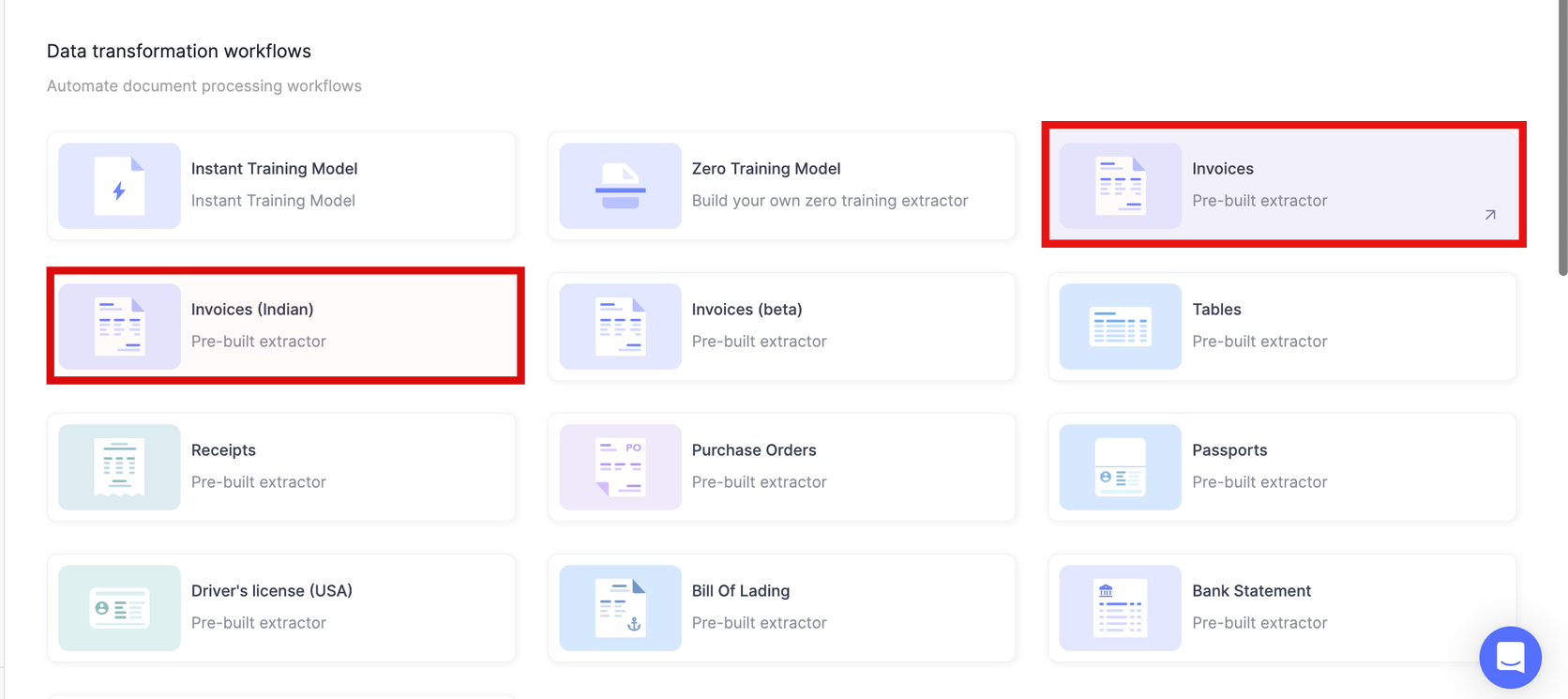
Step 2: Once you verify your email and log in, navigate to the 'Workflows' section and choose the pre-built AI invoice processing model.
Step 3: Establish approval rules and stages based on your requirements. Assign approvers to review flagged invoices.
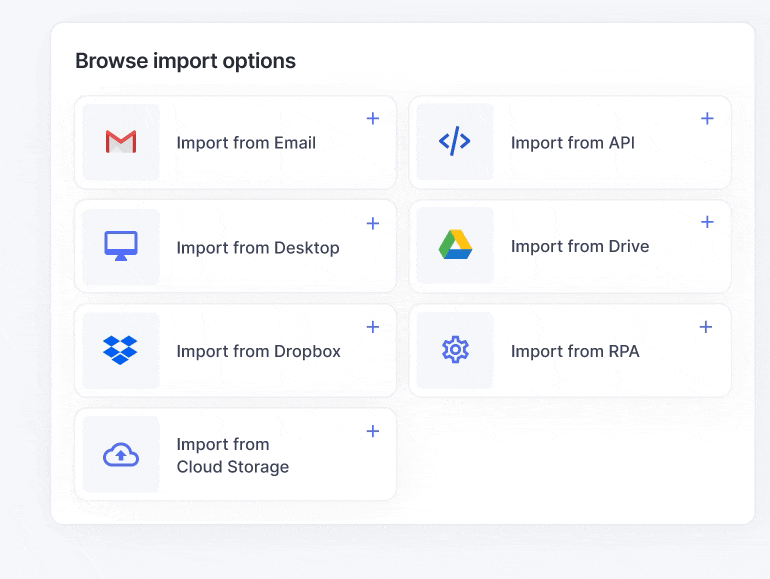
Step 4: Choose how invoices will enter the system: upload locally stored invoices (PDFs, JPG, PNG, etc.) or import files from different sources such as email or cloud storage like Google Drive, OneDrive, or Dropbox.
Here's a quick demonstration of how Nanonets extracts key data from a sample invoice
Step 5: The AI model automatically extracts crucial information such as vendor details, line items, and totals with exceptional accuracy. Review the extracted data and make necessary adjustments. Each correction you make improves model performance.
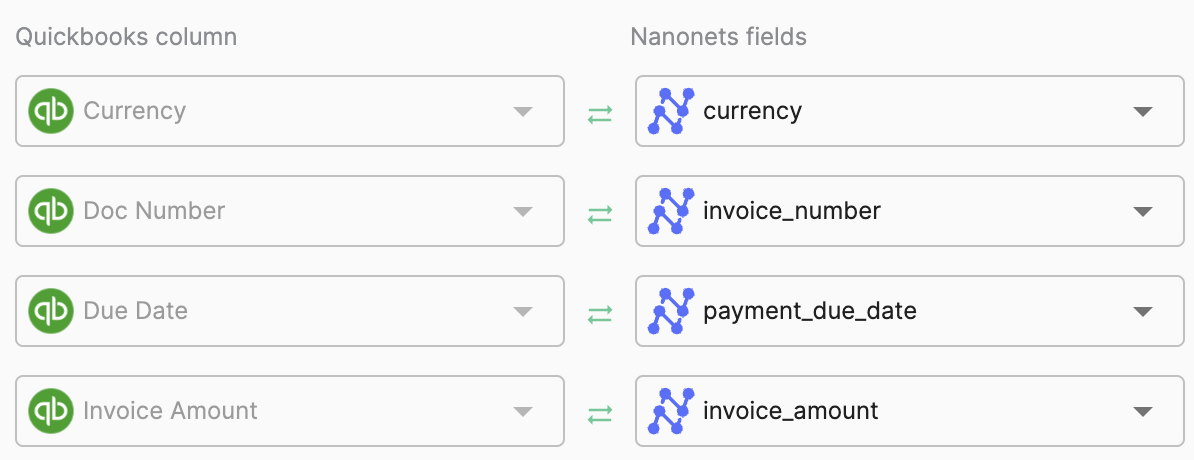
Step 6: Configure the automatic export and real-time synchronization of approved invoices to your accounting software or ERP. Nanonets integrates with QuickBooks, Xero, SAP, and more. You can also manually download the data in various formats or share it directly with team members. You can even automatically create journal entries in your accounting software or update inventory levels based on invoiced items.
Nanonets offers several advantages:
- No-code platform, making it accessible to non-technical users
- Highly accurate data extraction, even for complex invoice formats
- Continuous learning and improvement based on user feedback
- Robust security measures, including SOC-2 certification and GDPR compliance
- Flexible integration options with existing accounting and ERP systems
- Prebuilt AI invoice processing model that accurately extracts key information fields, such as vendor names, invoice numbers, and totals, out-of-the-box
- Customizable AI models that can be trained on your specific invoice formats and data requirements
The real-world impact of AI-powered invoice processing
Implementing Nanonets can make a huge difference. Here's what the folks at Tapi, a property maintenance company from New Zealand, had to say about their experience with Nanonets.
How does this translate into tangible benefits for businesses? Let's look at some real-world examples of how AI-powered invoice processing has made a difference for companies across various industries.
1. Tapi (New Zealand-based property maintenance company)
Tapi, managing over 110,000 properties, saw remarkable improvements after implementing Nanonets' AI invoice processing solution:
| Metric | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Invoice processing time | Reduced from 6 hours per invoice to just 12 seconds |
| Operational costs | Reduced by 70% |
| Data extraction accuracy | Achieved 94%+ accuracy |
| Scalability | Effortlessly handling invoices for 110,000 properties |
2. Ascend Properties (UK-based property management company)
Ascend Properties, which experienced 50% year-over-year growth, implemented Nanonets' AI tool for invoice processing:
| Metric | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Cost savings | 80% reduction in processing costs |
| Staffing efficiency | Reduced from a potential five full-time employees to 1 part-time employee |
| Processing time | Reduced from six hours a day to 10 minutes |
| Scalability | Managed growth from 2,000 to 10,000 properties without a proportional increase in staff |
These case studies demonstrate how AI-powered invoice processing can dramatically improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enable scalability for growing businesses. The impact goes beyond just time and cost savings – it allows companies to reallocate resources to more strategic tasks, improving overall business operations.
FAQs
1. How do I implement AI invoice processing in my business?
Start by choosing an Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) platform like Nanonets over LLMs or basic OCR tools. Sign up for the platform, select their pre-built invoice processing model, and configure your invoice import sources (email, cloud storage, direct upload). Set up approval workflows based on invoice amounts and departments, then integrate with your accounting software through APIs or direct connectors. Most IDP platforms are no-code solutions that deploy within days and continuously learn to improve accuracy over time.
2. What cost savings can I expect from AI invoice processing automation?
AI invoice processing typically reduces costs by 60-80%, dropping the average cost per invoice from $40.70 to $3.34. Processing time decreases from 16.3 days to 3.8 days on average. Real examples include Tapi reducing processing time from 6 hours per invoice to 12 seconds with 70% cost reduction, and Ascend Properties achieving 80% cost savings while reducing staff needs from 5 full-time employees to 1 part-time employee. Additional savings come from reduced errors (3-5% to <0.5%), eliminated duplicate payments, and staff reallocation to strategic tasks.
3. What is AI invoice processing and how does it differ from traditional methods?
AI invoice processing uses machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision to automatically extract, validate, and route invoice data without manual intervention. Unlike traditional manual processing that requires employees to type data and create templates for each vendor format, AI systems automatically adapt to any invoice layout and continuously improve accuracy. Traditional OCR only reads text, while AI understands context, relationships between data fields, and business rules to make intelligent decisions about routing and coding.
4. How does AI invoice processing handle three-way matching automatically?
AI automatically compares invoice data against purchase orders and receiving documents by analyzing item descriptions, quantities, and prices to identify discrepancies. The system handles variations like "Office Chair" vs "Ergonomic Office Chair Model X" and applies tolerance rules for quantity and price differences. When matches are within acceptable ranges, invoices are auto-approved. Discrepancies outside tolerance levels are flagged for manual review with detailed variance reports, while the system learns from historical approval patterns to improve accuracy.
5. What accuracy rates should I expect from AI invoice processing systems?
Modern AI invoice processing systems achieve 90-99% accuracy for standard invoices, with well-structured digital PDFs reaching 95-99% accuracy. Complex multi-page invoices or handwritten elements typically achieve 85-95% accuracy. Challenging scenarios like poor quality scans may see 70-85% initially. The key advantage is continuous improvement - systems typically start at 85-90% accuracy and improve to 95-99% for regular vendor invoices within 6 months as they learn your specific formats.
6. How does AI invoice processing integrate with accounting software like QuickBooks?
AI invoice processing platforms integrate with accounting software through direct API connections that enable real-time data sync. For QuickBooks, the system connects via OAuth, maps extracted fields to QuickBooks fields, and can automatically create bills, match vendors, and assign GL codes. Other supported platforms include Xero, SAP, NetSuite, and Sage. Advanced features include vendor matching, chart of accounts mapping based on invoice content, and automatic posting after approval with customizable field mapping.
7. Can AI detect duplicate invoices and prevent double payments effectively?
Yes, AI systems effectively detect duplicates by analyzing multiple criteria simultaneously: invoice numbers, amounts, dates, and vendor information. The system recognizes variations like vendor name differences ("ABC Corp" vs "ABC Corporation") and slight amount differences that might indicate OCR errors. When potential duplicates are identified, the system flags them for review with side-by-side comparison. Companies using AI duplicate detection report eliminating 95-99% of double payment incidents.
8. What are the main limitations of AI invoice processing technology?
Main limitations include dependency on document quality (poor scans or complex layouts reduce accuracy), challenges with handwritten text and unusual invoice designs, and a 2-4 week initial learning period. The technology requires integration setup for complex ERP systems and typically needs human review for 5-15% of invoices due to exceptions or low confidence scores. New vendor formats may require initial manual processing, and subscription costs can be significant for small businesses with low invoice volumes.
9. How do Large Language Models compare to dedicated IDP solutions for invoices?
LLMs offer flexibility and easy setup but produce inconsistent results, may hallucinate incorrect information, and lack structured workflows or security compliance for financial data. Dedicated IDP solutions provide consistent accuracy (95%+ vs variable for LLMs), built-in validation rules, complete workflow automation, and proper security measures. LLMs work for occasional manual processing, while IDP platforms are essential for high-volume business processing requiring reliability, integration, and compliance.
10. What ROI timeline can businesses expect from AI invoice processing implementation?
Most businesses achieve positive ROI within 8-10 months. Small businesses (100-500 invoices/month) typically break even in 3-6 months with $500-1,500 monthly investment generating $2,000-5,000 monthly savings. Medium businesses see 2-4 month payback periods, while enterprises often achieve ROI within 1-3 months. Long-term benefits include 200-400% ROI within the first year, with companies handling 300-500% more volume without proportional staff increases as the system matures.